Genital warts can affect anyone who is sexually active. While they’re common, the symptoms can be mild and even go unnoticed, so many people don’t even realise that these warts exist.
Although genital warts can go away on their own, they can cause discomfort and affect your sexual wellbeing if left untreated. Understanding what causes genital warts – including their symptoms and risk factors – is an important step towards getting the care you need to protect your sexual health.
Symptoms of genital warts
Genital warts are one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs),caused by certain types of the human papillomavirus (HPV), but most often types 6 and 11.
They are small growths or bumps that appear on the genital or anal area. Symptoms vary from person to person. Some people don’t even have any at all, while others develop visible warts. This is the main concern because without noticing them, the infection can spread easily and lead to complications. Knowing the symptoms helps you spot the signs early and get the right care.
These warts appear on both men and women with similar symptoms. The main difference lies in where they show up.
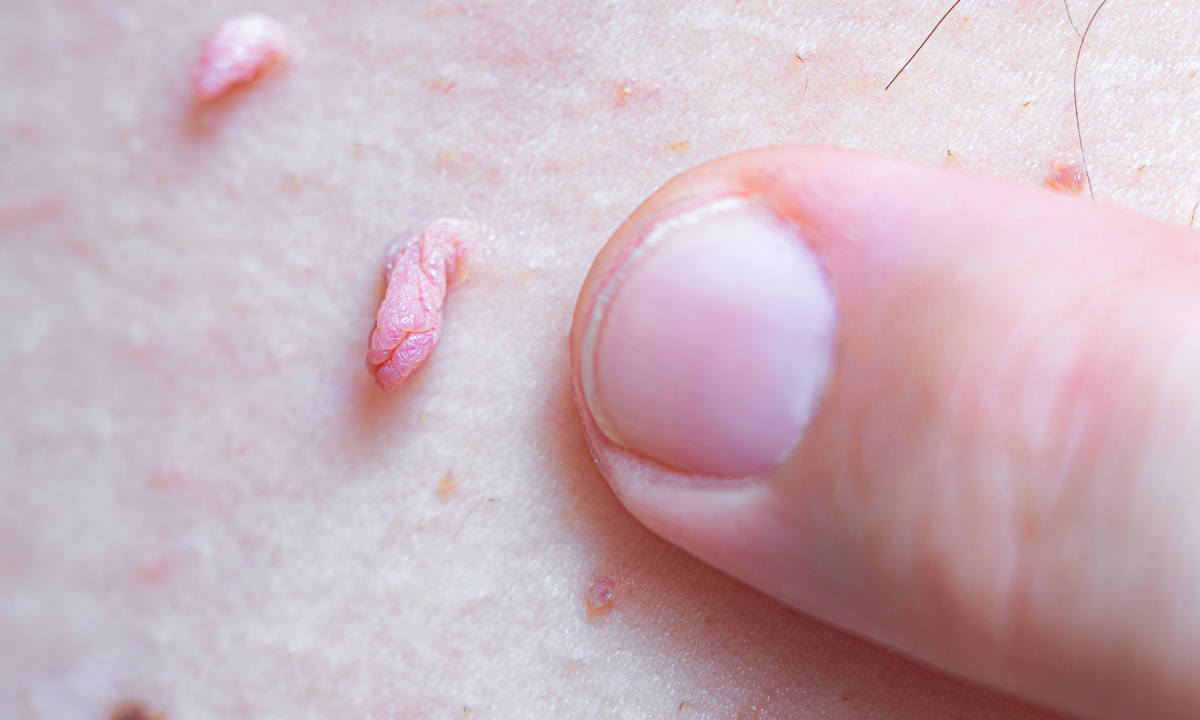
Female genital warts
In women, genital warts may appear on or around these areas:
Vulva (outer part of the female genitals)
Vagina (internally, which may be missed without an exam)
Cervix
Perineum (area between vagina and anus)
Anal area
Thighs
Symptoms may include:
Flesh-colored, white, pink, or gray bumps or growths
A cluster of warts that looks like a cauliflower
Itching, burning, or discomfort
Occasional bleeding after sex (if warts are on the cervix or inside the vagina)
Male genital warts
For men, these warts may appear on:
Penis shaft or glans (head)
Scrotum
Groin
Inner thighs
Around the anus
Inside the urethra (less common but possible)
The most common symptoms are:
One or more raised, flat, or cauliflower-like warts
Itching or irritation
Rarely, pain if warts are irritated
Once you notice any unusual bumps or changes in your genital area, along with an uncomfortable feeling, don’t hesitate to visit the sexual health clinics to get tested.
It’s normal to feel nervous and a bit awkward, but there’s nothing to worry about. Your doctor will understand and guide you through the diagnosis process.
Causes of genital warts
Genital warts are caused by infections with low-risk types of HPV, which include two main types:
HPV-6
HPV-11
The good news is that these types don't cause cervical cancer. However, you still need to be careful because they can lead to recurring outbreaks of warts.
HPV is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity, including:
Vaginal sex
Anal sex
Oral sex
Genital-to-genital rubbing (even without penetration)
Sharing sex toys
If you find any signs of genital warts, it’s also a good idea for your partner to get tested. They might have an HPV infection even without visible warts.
Your doctor will work with you to understand the cause of your infection and recommend a treatment that helps you prevent the warts from spreading or recurring.
Want to stay proactive about your sexual health? Request an appointment with Thomson Medical for STI screenings or consultation to ensure peace of mind and early detection.
Our specialists who can treat warts
Loading...
Who can get genital warts?
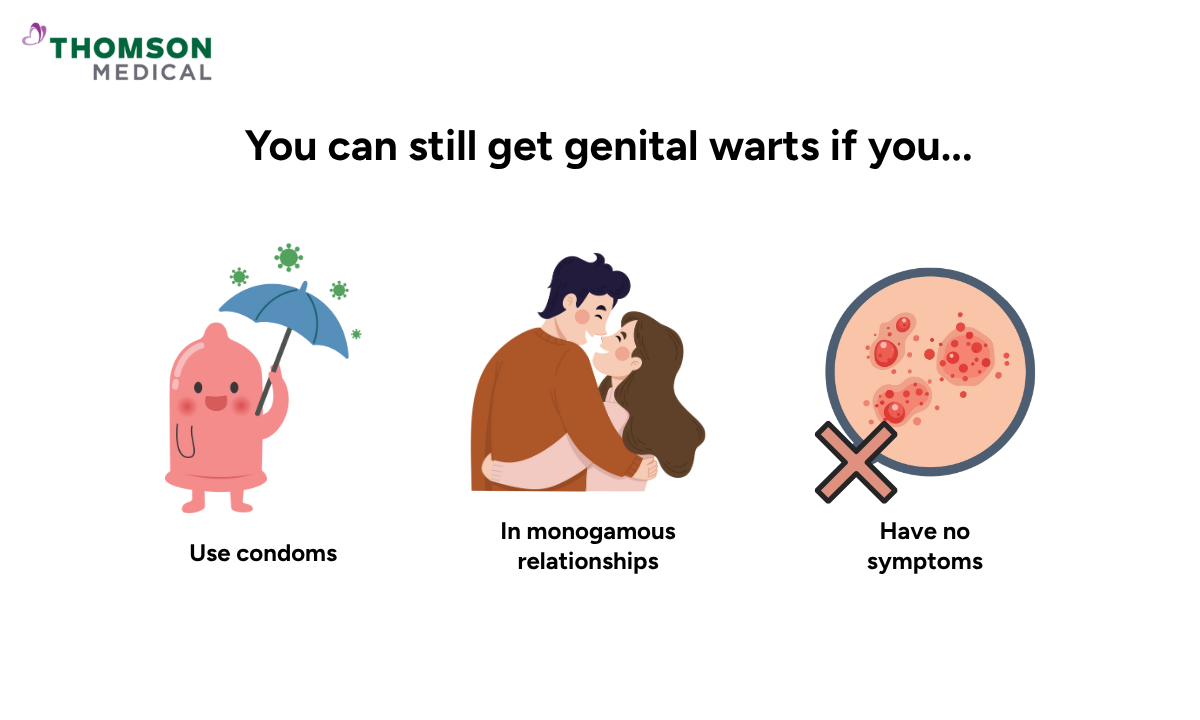
Genital warts are more common than people think. It doesn’t mean you're doing something wrong. Anyone who is sexually active can get genital warts, regardless of gender, sexual orientation, or number of partners.
Even people who use condoms can still get infected, as condoms don’t fully protect against skin-to-skin contact. Those in monogamous relationships can also be at risk because HPV can remain dormant for years. Even people with no symptoms can still carry and spread the virus without knowing it.
What are some risk factors?
Knowing the risk factors can help you better prevent genital warts and protect your health. While it’s common, you may be more likely to get warts if you:
Became sexually active at a younger age
Have multiple sex partners
Have a weakened immune system (e.g., from HIV or medications)
Don’t use condoms or dental dams
Smoke (which may affect immune response)
Have a partner who has HPV or genital warts
These warts are generally harmless, but they still need to be treated promptly. Without proper treatment, they can affect your daily life, causing discomfort, itching, and sometimes irritation in the genital area.
How soon do genital warts appear after infection?
Genital warts can appear weeks, months, or even years after exposure. Due to this delay, it’s very difficult to know exactly when or from whom the infection was acquired.
Some people never develop visible warts but can still carry and transmit the virus. That’s why regular check-ups help you stay on top of your overall health, detect the virus early, and prevent it from spreading or getting worse.
If you notice any signs of genital warts or have concerns about your sexual health, request an appointment with Thomson Medical today for further testing and personalised care.
FAQ
What are three symptoms of genital warts?
The three most common symptoms in both men and women include:
Fresh-colored or pink bumps on the genital or anal area
Itching, burning, or discomfort in the affected area
Clusters of warts that resemble cauliflower
Once your body has these symptoms, you should visit a clinic to get tested and receive appropriate advice from your doctor.
What is the first stage of genital warts?
In most cases, the first sign is a small bump or cluster that appears on the genitals, groin, or anus. You may also feel itching or irritation, though some people notice nothing at all initially.
For an accurate diagnosis, don’t hesitate to have an early check-up. Catching genital warts in the first stage can make a big difference. It’ll help prevent possible complications later on.
Do genital warts go away?
Yes. In many cases, these warts may go away on their own within months to a couple of years, especially if the immune system is strong. However, they can also recur, especially if the immune system is compromised.
Treatment can remove visible warts but does not eliminate the virus itself. In this case, make sure to get regular health check-ups to protect your sexual health.
What are the dangers of genital warts?
While genital warts caused by HPV-6 and 11 are not dangerous in terms of cancer, they can still affect your health in some certain ways.
Specifically, they can:
Cause emotional distress
Lead to discomfort or pain during sex
Occasionally grow large and obstruct the urethra, anus, or vaginal opening
Recur even after treatment
People with a weakened immune system (e.g., HIV-positive individuals) may experience more severe outbreaks.
What can be mistaken for genital warts?
There are some other conditions that may look like these warts, including:
Skin tags
Molluscum contagiosum (a viral skin infection)
Fordyce spots (harmless white bumps)
Pearly penile papules
Genital herpes (presents as painful blisters, not warts)
Syphilis sores or other STIs
Only a healthcare provider can make an accurate diagnosis. Based on your symptoms, your doctor will suggest a suitable test and treatment plan for you.
What do genital warts look like?
They may appear as:
Small, raised, flesh-colored bumps
Flat, smooth, or rough-textured
Single or in clusters
Sometimes resemble cauliflower heads
They can be itchy, but they’re usually not painful unless irritated.
Genital warts are common and treatable. If you notice any changes or symptoms, don’t panic. Instead, visit a sexual health clinic and see your doctor for advice. Regular check-ups, HPV testing, and vaccination can help you stay healthy, confident and worry-free about your sexual health.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice based on your unique circumstances, please consult a specialist at Thomson Medical. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Novena:
6592 6686 (Call), 8611 8986 (WA) - Bukit Batok:
6569 0668 (Call), 8686 3525 (WA) - Choa Chu Kang:
6893 1227 (Call), 8282 1796 (WA) Jurong:
6262 8588 (Call), 6262 8588 (WA)- Katong (female doctor):
6970 2272 (Call), 8611 9020 (WA) - Punggol:
6243 6843 (Call), 8811 0328 (WA) - Sembawang: 6753 5228
- Sengkang: 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): 6382 3313
- Tampines: 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: 6276 1525
