When you discover you're pregnant, one of the first things your doctor will look for on an early ultrasound is the gestational sac. This small, fluid-filled structure is the earliest visible sign that your baby is developing safely in the womb, appearing even before your baby's heartbeat can be detected.
What is the gestational sac?
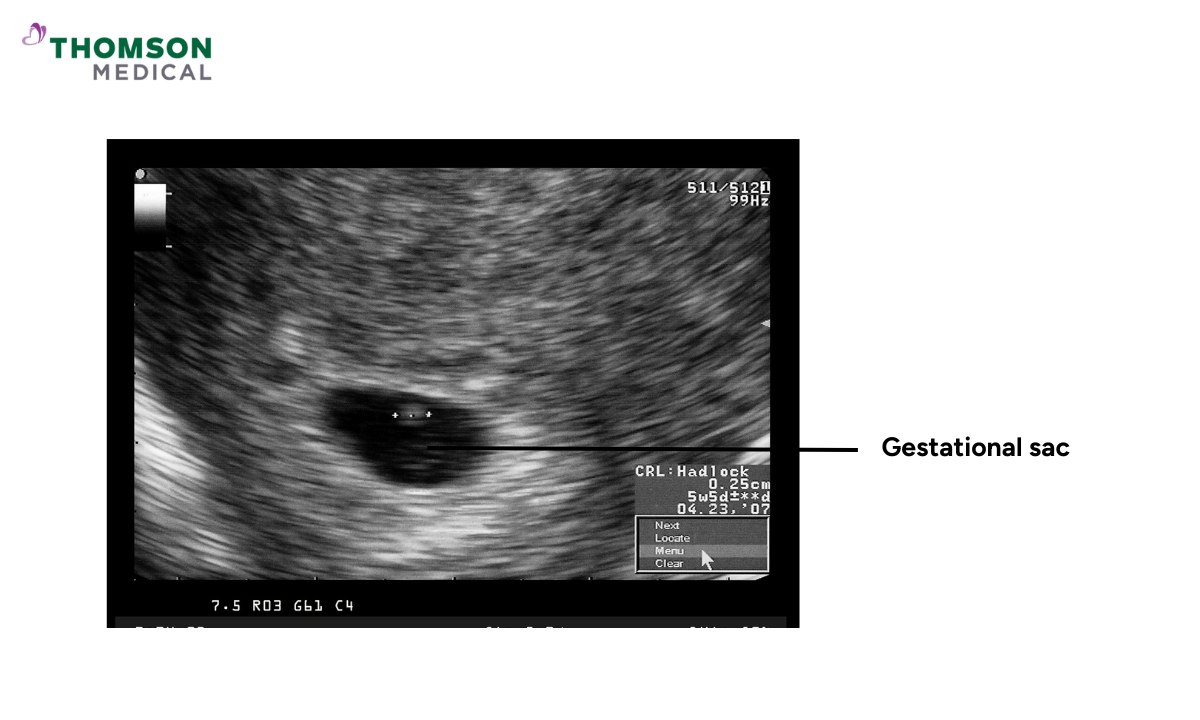
The gestational sac forms shortly after the fertilised egg implants in the lining of the womb. Filled with fluid, it provides a protective space that allows the baby to develop safely.
On an ultrasound scan, this space usually appears as a dark, rounded area. The darkness represents fluid, while the thin white rim around it is the early placenta, known as the chorionic membrane.
Detecting the gestational sac confirms that the pregnancy is developing inside the uterus (womb) and not elsewhere, which helps to rule out an ectopic pregnancy, that can be harmful if not treated promptly.
When does the sac form?
It generally forms around 4 to 4.5 weeks after the start of your last menstrual period. However, depending on the method of pregnancy scan you choose, the sac may be visible at different times. With a transvaginal ultrasound, for example, the gestational sac can often be seen as early as 4.5 to 5 weeks. While using a transabdominal ultrasound, the sac usually does not appear until 5.5 to 6 weeks.
Once the gestational sac is visible, another structure called the yolk sac will start to develop inside it. The yolk sac feeds the embryo and helps in the formation of its first blood cells. On ultrasound, it’s visible as a little white ring inside the gestational sac.
In addition to the gestational sac and yolk sac, at around 6 to 6.5 weeks of pregnancy, you may also see the foetal pole (your baby's earliest visible form). The foetal pole appears as a line- or oval-shaped structure near the yolk sac, measuring about 1 to 2 millimetres.
What happens if no gestational sac is seen on ultrasound?
Sometimes, a woman may have a positive pregnancy test, but the scan shows no gestational sac. Although this may be worrying, it doesn’t usually mean that something is wrong. Possible reasons include:
The pregnancy is too early, meaning ovulation may have occurred later than expected, making the pregnancy younger than estimated.
Another possibility is ectopic pregnancy, where the pregnancy develops outside the womb, most often in a fallopian tube, meaning the sac is not visible in the womb.
Miscarriage, where a pregnancy starts but does not continue to develop, may also explain the absence of a sac.
To clarify the situation, your doctor may repeat hCG blood tests 48 hours apart to look for appropriate changes in hormone levels. A repeat scan after 5-7 days can help to provide clearer answers.
If you have questions about your early pregnancy scan results or need clarification on what a gestational sac finding means, schedule an appointment with Thomson Women's Clinic. Our O&G specialists can provide tailored recommendation based on your pregnancy condition.
Our O&G doctors in Singapore
Loading...
Gestational sac abnormalities
Several findings on an early pregnancy ultrasound may raise concerns. Understanding what they mean can help you know what to expect and when follow-up care is needed.
Empty gestational sac
Occasionally, a gestational sac may be seen but appears empty, with no yolk sac or foetal pole inside. If this continues past 6.5 to 7 weeks, there are two possible explanations:
Blighted ovum (anembryonic pregnancy):
The embryo either did not develop at all or stopped growing very early, even though the gestational sac continued to develop.
The pregnancy is earlier than expected:
The pregnancy may be younger than estimated, meaning the yolk sac and foetal pole have not yet appeared.
Because timing makes such a difference, doctors often wait and rescan before making a final diagnosis. Sometimes, what looked empty or concerning at first later shows normal growth.
Irregular gestational sac
A healthy gestational sac is usually smooth and spherical or oval in shape, with firm, thick walls. However, if any of the following features are observed, it may be cause for concern:
An odd or collapsed shape
Extremely thin walls (less than 2 mm)
An off-center yolk sac inside the gestational sac
The sac wall wrinkles or folds
Since such findings could potentially indicate a miscarriage, inadequate implantation, or ectopic pregnancy, it’s important to monitor your pregnancy with follow-up scans to assess how it develops.
Missing or abnormal yolk sac
The yolk sac has a crucial role before the placenta takes over. It supplies nutrients to the embryo and helps in the formation of early blood cells. A typical yolk sac is smaller than 6 mm across and is a well-defined sphere.
Concerns may arise if:
It’s not visible after 5.5-6 weeks, which may indicate a failed pregnancy
A yolk sac larger than 6 mm is linked to an increased risk of miscarriage
Malformed yolk sac can be associated with chromosomal issues or poor embryo growth
However, a single abnormal scan doesn't necessarily determine the outcome. Your doctor will monitor you closely with repeat ultrasounds before confirming the outcome.
Early pregnancy scans with Thomson Medical
Finding out that you're pregnant can be both exciting and unnerving, but with the right care and guidance, you can get through this uncertain time. At Thomson Medical, we understand the concerns that would be mothers face. We offer pelvic ultrasound scans (both transvaginal and transabdominal) to confirm your pregnancy and monitor early development.
If your initial scan reveals an empty gestational sac or any other irregular findings, we can provide follow-up scans to monitor your pregnancy. In addition, we also provide hCG blood tests to track your pregnancy hormone levels and help determine the next steps.
We recommend starting antenatal care at around 6 to 8 weeks, as this helps to detect pregnancy complications and ensure that mothers receive the right care and support at the right time. Knowing about your pregnancy health early on also means you can make informed decisions about any issues that may arise during pregnancy.
If you have any concerns about abnormalities or other issues during the early stages of pregnancy, schedule an appointment with Thomson Women’s Clinic. Our O&G specialists could help by providing ultrasound scan and answering your questions.
FAQ
What does it mean when there is a gestational sac but no foetal pole?
It often means the pregnancy is still early. The foetal pole usually appears by 6 to 7 weeks. If it remains absent after 7 weeks with a normal sac size, the result may suggest a blighted ovum. Doctors usually arrange another scan and hCG testing before confirming.
Can you have a gestational sac without a foetus?
Yes. At the very start, the embryo may not yet be visible. The embryo in a blighted ovum either never develops or stops very early, but a gestational sac grows.
Can a gestational sac be hidden?
Occasionally. If the womb tilts backwards (a retroverted uterus) or the mother has a higher body mass index, the sac may be harder to see on an abdominal scan. In such cases, a transvaginal ultrasound gives clearer images.
What if hCG levels are high but no foetal pole is seen?
This can point to an ectopic pregnancy or a blighted ovum, but it may also simply mean ovulation occurred later than thought. Doctors usually repeat hCG blood tests and schedule follow-up scans to confirm.
How late can a foetal pole develop?
Normally the foetal pole is visible by 6 to 6.5 weeks. In some pregnancies, particularly if ovulation was late, it may not appear until 7 to 7.5 weeks.
What are the symptoms of an empty gestational sac?
Often, there are no symptoms at all. Some women may notice light bleeding, mild cramping, or a sudden fading of pregnancy symptoms like nausea or tender breasts. Ultrasound is the only way to confirm.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice based on your unique situations, please consult a specialist at Thomson Medical. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Novena:
6592 6686 (Call), 8611 8986 (WA) - Bukit Batok:
6569 0668 (Call), 8686 3525 (WA) - Choa Chu Kang:
6893 1227 (Call), 8282 1796 (WA) Jurong:
6262 8588 (Call), 6262 8588 (WA)- Katong (female doctor):
6970 2272 (Call), 8611 9020 (WA) - Punggol:
6243 6843 (Call), 8811 0328 (WA) - Sembawang: 6753 5228
- Sengkang: 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): 6382 3313
- Tampines: 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: 6276 1525
