What is hand surgery?
Hand surgery refers to a range of procedures performed to treat injuries or disorders affecting the bones, joints, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and soft tissue of the hand and wrist. It is usually used to treat conditions such as fractures, tendon lacerations, arthritis, ganglion cysts, deformities, or nerve injuries.
Depending on the condition, surgery might involve bone realignment, tendon or nerve repair, joint reconstruction, or removal of abnormal growths. The goal is to relieve pain, restore hand function, and improve mobility and strength when non-surgical treatments are no longer effective.
Why do I need hand surgery?
Hand surgery may be recommended if you have:
Ongoing pain
Stiffness
Deformity
Nonsurgical treatments such as splinting, physiotherapy, or medications don't improve the weakness in your hand or wrist.
Surgical intervention may be needed to restore movement, reduce pain, or prevent long-term damage for conditions such as:
Tendon injuries
Fractures
Ganglion cysts
Dupuytren’s contracture
Advanced arthritis
Surgery may also be needed after trauma or to correct congenital or degenerative deformities that interfere with daily activities or quality of life.
What are the different types of hand surgery?
Hand surgery encompasses several procedures tailored to address specific injuries or conditions affecting the hand, wrist, and fingers. Here are some of the most common types:
Tendon repair
Tendon repair surgery in the hand involves repairing torn or damaged tendons, often due to injury. The procedure aims to restore movement and function to the affected area. It can involve suturing the tendon ends together, and in some cases, grafting healthy tendon tissue. Post-operative care includes immobilisation with a splint and physical therapy to regain strength and range of motion.
Fracture fixation
Fracture fixation in the hand involves surgical procedures to repair and stabilise broken bones, primarily when conservative treatments like splinting or casting are insufficient.
This often involves open reduction (realignment of the bone through an incision) and internal fixation (using screws, plates, or pins to hold the bone fragments in place). The goal is to restore proper bone alignment and promote healing, ultimately allowing for functional hand recovery.
Joint fusion (Arthrodesis)
Joint fusion, also known as arthrodesis, is a surgical procedure where two or more bones in a joint are fused to become one, eliminating movement in that joint. In the hand, this procedure is often performed to relieve pain from arthritis by eliminating the painful joint space and rubbing of bone surfaces. While it provides pain relief, it does result in a loss of movement in the fused joint.
Joint replacement (Arthroplasty)
Joint replacement in the hand, also known as arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure that replaces a damaged joint with an artificial implant to relieve pain and restore function. This is commonly performed on the knuckles (metacarpophalangeal or MCP joints) and the joints at the base of the fingers (proximal interphalangeal or PIP joints). The procedure is often considered for arthritis, trauma, or other conditions causing joint deterioration.
Nerve repair or grafting
Nerve repair and grafting in the hand involve surgical procedures to restore nerve function after injury. Nerve repair, or coaptation, aims to reconnect severed nerve ends directly, while nerve grafting bridges gaps with tissue from another part of the body or a donor. Nerve transfers, a different approach, reroute healthy nerves to restore function to the damaged nerve.
Each of these procedures addresses a different need, and outcomes vary depending on the severity of the condition and your overall hand health. Your doctor will recommend the most suitable option based on your individual case.
Disclaimer: The information provided is for general knowledge only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice.If you're experiencing any of these symptoms, request an appointment with our specialists at Thomson Medical for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
What is the cost of hand surgery in Singapore?
Costs for hand surgery in Singapore vary significantly depending on whether you choose a public or private hospital.
Hand surgeries are under TOSP codes SB704H, SB802H, SB703H, SB713H, SB801H, SB835J, SB708W, SB803J, SB802J, and SB714W.
Day surgery
The information for private hospitals about the cost of hand surgery is between SGD 10,953 and SGD 18,302 for day surgeries based on the SB704H fee benchmarks.
Inpatient surgery
For inpatient surgeries, the cost will range from SGD 17,334 to SGD 25,760 at private hospitals.
MOH provided a breakdown of the fees for private hospitals and clinics as per SB704H—Hand, Closed Fracture, ORIF/Plate And Screws (Single), Joint/Non-Joint.
Breakdown of Fees
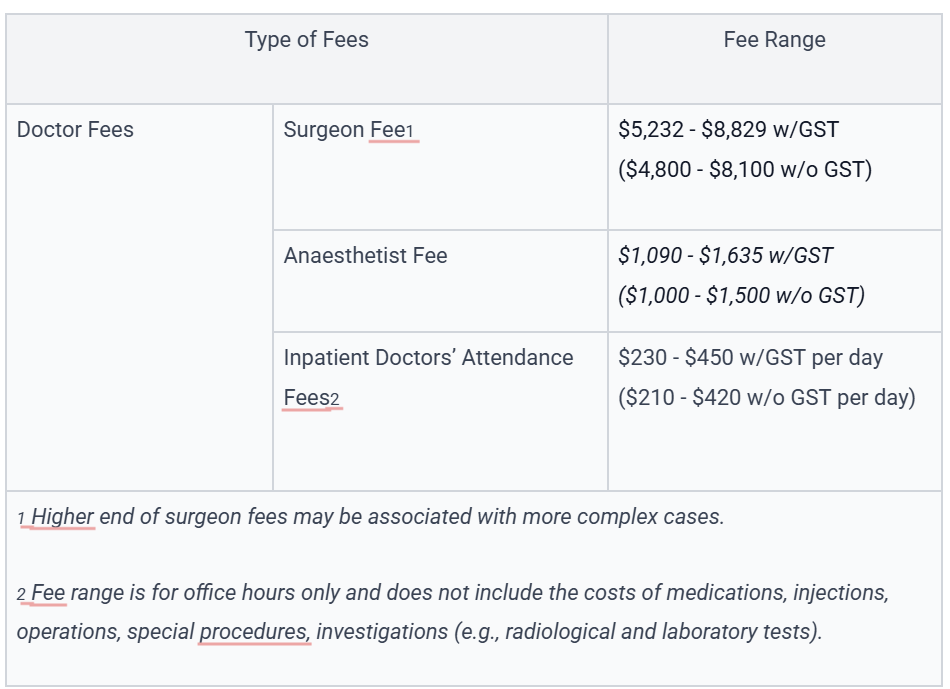
However, additional charges may arise from expenses such as pre-surgery consultations, imaging tests like X-rays or CT scans, medications, post-surgery follow-up appointments, and extended rehabilitation.
This article was written in May 2025. Hence, prices for hand surgery may have changed since then. For more accurate benchmarking prices, please visit the MOH website for more details.
Are there any subsidies for hand surgery?
Yes, there are several schemes in Singapore that can help offset the total costs of hand surgery.
These include MediSave, MediShield Life, and Integrated Shield Plans. Each offers different levels of coverage for your hand surgery, depending on your eligibility and insurance arrangements.
MediSave
MediSave is a national medical savings scheme that allows Singaporean citizens and permanent residents to use their savings for hospitalisation expenses.
For hospitalisation, you can use up to SGD 1,130 per day for the first two days and SGD 400 per day for subsequent days for inpatient hospital charges. These charges include daily ward changes, treatment fees, investigations, and medicines.
For day surgery, you can claim up to SGD 830 per day for hospital charges related to the procedure. For surgery, you can use between SGD 240 and SGD 5,290 from your MediSave, depending on the complexity of the surgery.
According to the CPF website, hand surgery under SB704H is classified under 3C on the Table of Surgical Procedures (TOSP). Hence, the withdrawal limit for hand surgery is SGD 1,920.
This article was written in May 2025. Hence, prices for hand surgery may have changed since then. For more accurate benchmarking prices, please visit the CPF website for more details.
MediShield Life
MediShield Life is a basic health insurance plan for all Singaporeans and PRs, designed to help pay for large hospital bills and selected costly outpatient treatments.
It will cover a portion of the surgical and hospitalisation costs for hand surgery, and similar to MediSave, there are claim limits.
For hospitalisation, the claim limits are SGD 830 per day for normal wards and SGD 5,140 for intensive care unit (ICU) wards, which include an additional SGD 800 per day for the first two inpatient days.
For surgical procedures, MediShield Life also follows the TOSP, meaning that there will be a claim limit for hand surgery at SGD 1,920 if your hand surgery is under SB704H.
This article was written in May 2025. Hence, prices for hand surgery may have changed since then. For more accurate benchmarking prices, please visit the CPF website for more details.
Integrated Shield Plans
Integrated Shield Plans (IPs) are private insurance policies that offer additional coverage beyond what is provided by MediShield Life. They can cover a larger portion of your hospital bill, especially if you opt for private hospitals or higher-class wards.
Many IPs also offer “as-charged” benefits, meaning they cover the actual bill amount, subject to policy terms and annual limits.
Coverage details and claim limits vary depending on the insurer and the specific plan and additional riders purchased.
If you are curious how much you can claim from your IPs for your hand surgery, it is best to talk to your insurance provider directly to discuss the details of your plan. For those under Prudential, please contact us via the Prudential medical concierge form if you have any further questions.
What factors affect the cost of my hand surgery?
Several key factors influence the final bill for hand surgery in Singapore:
Pre-surgery expenses
Initial consultation fees
Diagnostic imaging tests
Pre-operative assessments
Specialist referrals (when necessary)
Surgery-related costs
Surgical fees and anaesthesias
Medical devices and implants (when necessary)
Day surgery vs inpatient costs
Post-surgery expenses
Follow-up consultations
Physiotherapy sessions
Wound care supplies
Orthopaedic Surgeons at Thomson Medical
Loading...
Case Study: Private Hospital with Integrated Shield Plan
Profile: A 38-year-old office worker fractured a bone in his hand after slipping on wet stairs. Since it was his dominant hand, typing and daily tasks became painful and difficult.
After an X-ray and a visit to a hand specialist, he was advised to have surgery to realign and stabilise the bones using a small metal plate and screw. The surgery was done in a private hospital, and he was able to go home the same day.
| Estimated total bill | Insurance coverage | Final out-of-pocket expenses |
|---|---|---|
| SGD 10,953 to SGD 18,302* | Since 2019, the Ministry of Health (MOH) has mandated that all new IP riders include a minimum 5% co-payment—to encourage prudent use of healthcare services and avoid overconsumption.
| The patient would need to pay from SGD 548 to 915, which can usually be covered by MediSave.
|
Please note that for the most accurate estimate of insurance coverage and out-of-pocket expenses, you should consult your doctor and insurance provider directly, as coverage details vary by plan and insurer.
*This article was written in May 2025. Prices for hand surgery are currently not available for private hospitals, so an estimate was included. The details may have changed since then. For more accurate benchmarking prices, please visit the MOH website for more details.
How do I process my insurance claims?
To process an insurance claim at a hospital in Singapore, you typically need to inform the hospital staff of your intent to claim, gather required documents like final bills and receipts, and submit the claim to your insurance provider through their designated channels (online portal, email, etc.).
For some insurance policies, the hospital may handle the claims process directly, especially for cashless claims. Here's a more detailed breakdown:
Understand your coverage:
Before you schedule your treatment, meet up with your financial advisor to discuss the costs and coverage available for you should you undergo hand surgery.
Inform the hospital:
When you are admitted to the hospital, inform the hospital staff that you wish to make an insurance claim. They may guide you through the necessary paperwork and forms.
Gather the required documents:
Ensure you have all the original, final bills and receipts for all treatments, including hospital stays, procedures, and medications.
If available, gather any relevant medical reports, diagnostic test results, and discharge summaries.
If you used your MediSave account for payment, you'll need a statement showing the Hospital Registration Number (HRN).
You may need to download and complete a claim form from your insurance provider's website.
Submit the claim:
Many insurers offer different portals for submitting claims, including online portals, mobile apps, email, or direct paper submission to your financial advisor.
If the hospital handles the claim directly, they will submit it on your behalf.
Follow up and track progress:
You should receive an acknowledgement of your claim submission.
Check the status of your claim through your insurer's online portal or app.
Do note that claim processing typically takes about 2 to 3 months from the date of submission (e-filing).
Some complex cases may take longer, especially if additional documents or clarifications are required.
If you don't receive updates after 3 months or have more questions, contact your insurer or the hospital for assistance.
At Thomson Medical, the insurance claims process is streamlined for your convenience.
The hospital provides e-filing services, submitting claims directly to MediSave, MediShield Life, and Integrated Shield Plan providers on your behalf.
This approach reduces paperwork and ensures claims are processed efficiently, allowing you to focus on recovery.
FAQ
What is the recovery time for hand surgery?
Recovery depends on the type of procedure, but stitches are often removed within 1 to 2 weeks. You may notice swelling, stiffness, or soreness during early healing. It can take several weeks to a few months to regain full hand function and longer if tendons, joints, or bones were involved. Full strength may take several months to return, especially with more complex repairs.
How painful is hand surgery?
Some discomfort is normal, especially in the first few days. Because surgery may involve bones, tendons, or ligaments, pain can range from mild to moderate, depending on the procedure. Medication and hand elevation usually help manage pain in the short term, and most patients feel better week by week.
Is it worth getting hand surgery?
Surgery is usually recommended when non-surgical options like splints, injections, or therapy haven’t helped and when pain, stiffness, or loss of function begins to affect daily life. In many cases, surgery can improve mobility and reduce long-term discomfort.
Do you lose hand strength after surgery?
Temporary weakness is common after hand surgery. Some patients notice reduced grip strength or coordination early on, but this typically improves with physiotherapy and daily hand use. With proper care, most people regain their strength over time.
When is it too late for hand surgery?
It's rarely too late. Even if your symptoms have been ongoing for months or years, surgery may still offer relief. That said, earlier treatment can lead to better outcomes—so don’t delay if hand function or pain is getting worse.
Can hand injuries heal on their own?
Some minor injuries or strains can recover with rest, ice, and splinting. However, conditions involving torn tendons, displaced fractures, or progressive deformities usually do not heal properly without surgical intervention. It’s best to consult a hand specialist for a personalised assessment.
Disclaimer: The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice on pricing and services, contact us at Thomson Medical today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Medical Concierge
- 8.30am - 5.30pm
- WhatsApp: 9147 2051
Need help finding the right specialist or booking for a group?
Our Medical Concierge is here to help you. Simply fill in our form, and we'll check and connect you with the right specialist promptly.
Notice:
The range of services may vary between Thomson clinic locations. Please contact your preferred branch directly to enquire about the current availability.
Get In Touch