It's completely natural to feel a bit anxious or uncertain when it comes to STI testing. You might worry about what the results will show or feel uncomfortable discussing sexual health. But the reality is that STIs are common, and many show no symptoms at all in the early stages. Getting tested when you're sexually active is normal, taking care of yourself whether you're here for yourself or supporting someone you care about.
What is a sexually transmitted infection (STI)?
A sexually transmitted infection (STI) is an infection that passes from one person to another primarily through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Some STIs can also spread through non-sexual means, such as blood transfusions, shared needles, or from mother to baby during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
You may have heard the term STD (sexually transmitted disease) before. They're often used interchangeably, however, STI is more accurate because you can have an infection without showing any disease symptoms.
What are the causes of STIs?
STIs are caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungi that spread through sexual contact, bodily fluids (blood, semen, vaginal fluid). Close skin-to-skin contact can also spread some STIs even when you're using protection.
Knowing what type of infection you have helps determine the right treatment approach:
Bacterial STIs, such aschlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis
Viral STIs, like HIV, herpes, HPV, and hepatitis B
Parasitic STIs, including trichomoniasis, pubic lice, and scabies
Fungal STIs, such as candidiasis (a yeast infection), are less common and not always considered to be strictly STIs
Are STIs contagious?
Yes, STIs can be passed from one person to another during sexual activity. Some infections, such as HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C, can also be transmitted through blood contact or from a mother to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
How common are STIs?
STIs are more common than many people realise.According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 1 million STIs are acquired every day globally. In Singapore, 2,719 people were newly diagnosed with chlamydia (one of the most common STIs) in 2018.
These numbers show that if you have an STI, you're not alone, and seeking care is a responsible step.
Who's most at risk of STIs?
Anyone who is sexually active can get an STI, no matter your age, gender, or sexual orientation. However, certain factors can increase your risk:
Having an intercourse without using a condom
Having multiple sexual partners
Being a teenager or young adult
Having had an STI before
Having a weak immune system
These are just risk factors and they don't define who you are. They’re meant to guide your doctor in providing the most appropriate care for you.
Our specialists
Loading...
What symptoms should you watch for?
A common misconception about STIs is that they always show symptoms, but many STIs can have no symptoms at all.When symptoms do show up, they might include:
Painful or burning sensation when you pee
Sores, bumps, or blisters on your genitals
Unusual discharge from your penis or vagina
Irritation or itching in the genital area
Pelvic pain
Flu-like symptoms like fever or swollen glands
Symptoms of specific STIs
Different STIs can present in different ways. Here's what to look out for:
Gonorrhoea and chlamydia:
Unusual discharge, burning or cloudy urine
Both can also infect the throat or rectum, often without any symptoms
If present during childbirth, it may cause red and sore eyes in the baby
Syphilis:
The first sign is usually a single, painless sore
You might get a rash on the body, mouth, palms, or soles of feet
Trichomoniasis:
Abnormal vaginal discharge
Redness of the vulva (outside part of the female genitals)
Itching and painful intercourse
Genital herpes (HSV):
Painful sores, blisters, or ulcers on genitals or around the mouth
Infection stays in the body for life and can return
Often no noticeable symptoms
Certain strains cause small bumps in the genital area
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV):
Early infection may have no symptoms, or flu-like symptoms such as fever, sore throat, fatigue, or swollen glands
If you have concerns about possible STI symptoms, or would like to be proactive about your sexual health, you may request an appointment for confidential check-up with Thomson Medical. Our doctors offer testing, clear diagnosis, and supportive care to help you safeguard your health and that of your loved ones.
How are STIs tested?
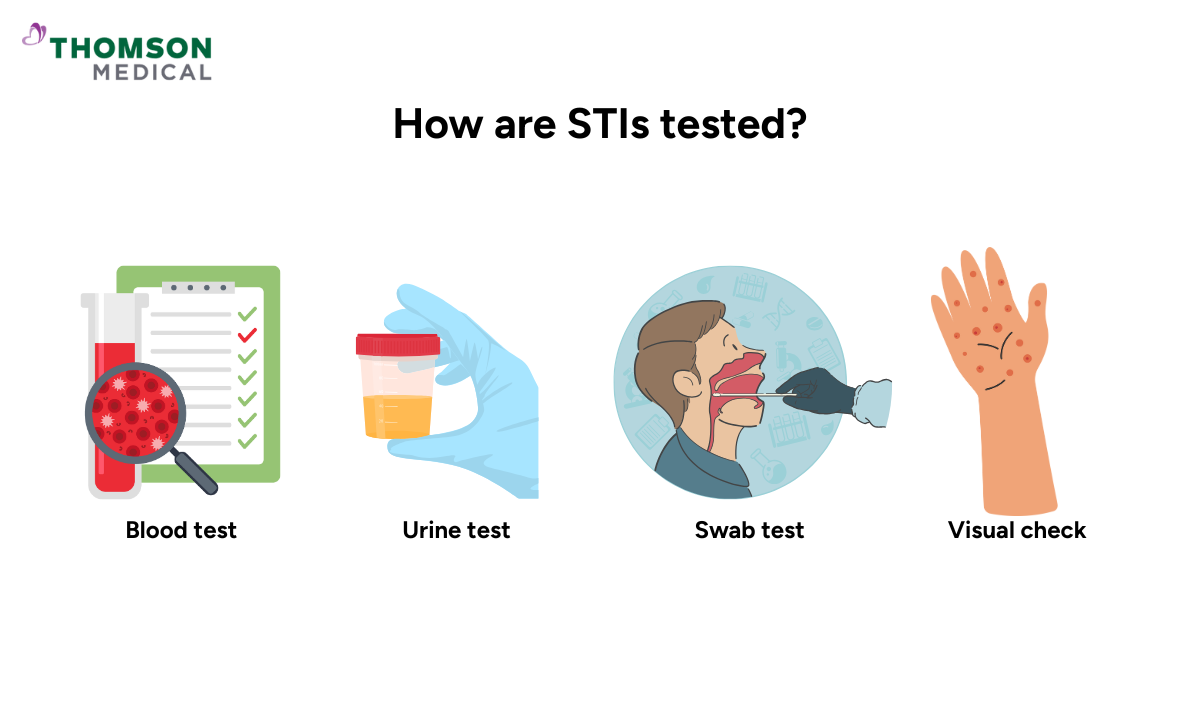
Diagnosis and testing are straightforward, and there's nothing to worry about. Your doctor will suggest the right tests for you based on the symptoms you may have.
Common STI tests include:
Blood test for HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis
Urine test for chlamydia and gonorrhea
Swab test from your genitals, throat, or anus
Visual check for any sores, rashes, or lice
Feeling nervous about the exam is completely normal. Your doctor understands and walks you through the examination to make you feel comfortable.
What are the treatment options for STIs?
The good news is that many STIs can be effectively treated, and all can be managed. With proper care, people go on to live healthy lives and relationships.
Treatments are depend on the type of infection:
Bacterial STIs can usually be cured completely with a round of antibiotics.
Parasitic STIs are treated with antiparasitic medicines and can also be cured.
Viral STIs can’t be cured, but antiviral medicines can control them, easing symptoms and lowering the chances of transmission.
Your doctor will work with you to find the treatment plan that fits your needs and lifestyle.
Why is STI testing important?
Regular STI testing is one of the most important steps you can take for your sexual health. Here's why it matters:
Early detection prevents complications, even before symptoms appear
Early treatment protects your fertility
Reduce transmission and protect your partners
Testing in pregnancy keeps both mother and baby safe
Regular testing gives you peace of mind
What happens if STIs are left untreated?
Early treatment makes a real difference, and it's never too late to start. Without treatment, some STIs can lead to complications like:
Lower chances to have a child
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), an infection of the female reproductive organs
Higher risk of catching or spreading HIV
Pregnancy complications such as miscarriage, premature birth, or infection
Certain cancers, particularly from HPV-related
Chronic pain or organ damage in rare cases
You can avoid these complications. If you've been diagnosed with an STI, know that starting treatment at any stage helps protect your health and wellbeing.
Ways to protect yourself from STIs
Taking steps to protect your sexual health benefits everyone involved.Here are ways to protect yourself from getting an STI:
Use condoms or dental dams during sexual intercourse
Consider limiting your number of sexual partners
Get vaccinated against HPV, and hepatitis A and B
Don't share needles
Get tested regularly, especially if you have have multiple partners
Talk openly with partners about sexual health
Schedule routine check-ups with your healthcare provider
Remember that looking after your sexual health is a normal part of self-care, not something to feel embarrassed about.
If you have concerns about STI symptoms or want to take a proactive approach to your sexual health, Thomson Medical is here to help. Request an appointment for testing, diagnosis, and supportive care in a judgment-free environment.
FAQ
What causes an STI?
STIs are caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungi that pass between people during intercourse (vaginal, anal, or oral). Some can also spread through shared needles, blood contact, or from mother to baby during pregnancy and birth.
Are STI and STD the same?
Not exactly. An STI (sexually transmitted infection) is when you have the infection in your body, even if you're not showing symptoms. An STD (sexually transmitted disease) is when that infection causes noticeable symptoms or health problems. Since lots of infections don't produce symptoms, STI is the more accurate term.
What are the 7 most common STIs?
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, trichomoniasis, HPV, herpes, and HIV are the ones you'll hear about most often.
What happens if you have an STI?
Some STIs can be completely cured with treatment, while others require ongoing management. With the right treatment, people with STIs live healthy lives and have meaningful relationships. However, infections that go untreated for long periods can sometimes lead to fertility challenges, chronic illness, or other serious complications.
How can you tell if someone has an STI?
You can't just by looking. Many STIs have zero visible symptoms, which is why they're sometimes called "silent infections." Testing is the only reliable way to know for sure.
Can STIs be cured?
It depends on the type. Bacterial STIs (like chlamydia and gonorrhea) and parasitic ones (like trichomoniasis) are curable with medication. Viral STIs (like HIV and herpes) stay in your body, but the appropriate treatments can help keep them under control so you can stay healthy and minimize the risk of passing them on.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice based on your unique situations, please consult a specialist at Thomson Medical.Request an appointment with Thomson Medical today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Novena:
6592 6686 (Call), 8611 8986 (WA) - Bukit Batok:
6569 0668 (Call), 8686 3525 (WA) - Choa Chu Kang:
6893 1227 (Call), 8282 1796 (WA) Jurong:
6262 8588 (Call), 6262 8588 (WA)- Katong (female doctor):
6970 2272 (Call), 8611 9020 (WA) - Punggol:
6243 6843 (Call), 8811 0328 (WA) - Sembawang: 6753 5228
- Sengkang: 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): 6382 3313
- Tampines: 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: 6276 1525
