What is tubal ligation?
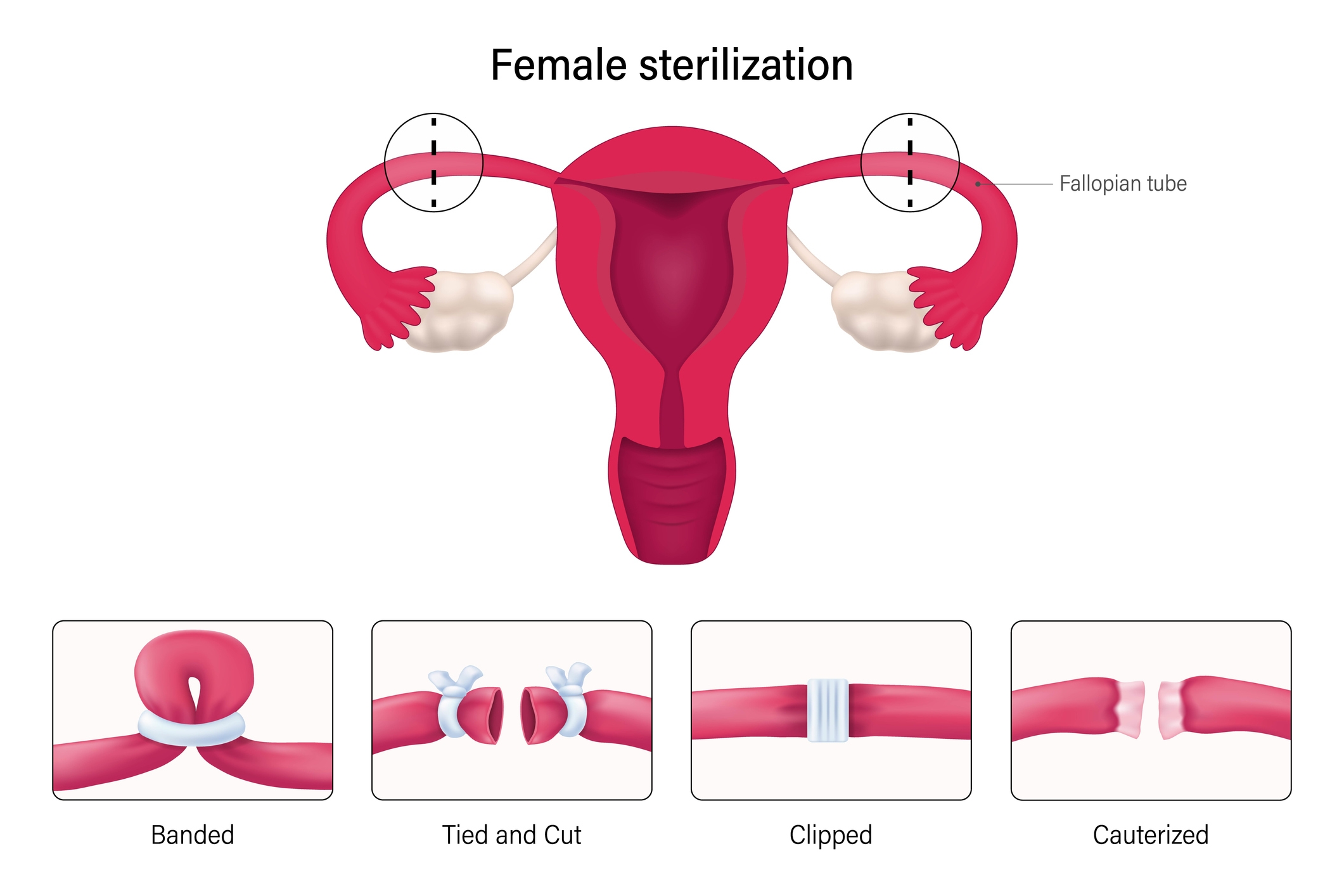
Tubal ligation, also known as female sterilisation, is a permanent method of birth control. In tubal ligation, both the fallopian tubes are removed, cut and tied with special thread, closed shut with bands or clips, or sealed with an electric current. This procedure prevents the sperm from reaching the egg, thus preventing pregnancy.
Note: Bilateral tubal ligation (BTL) and tubal ligation both refer to the same procedures, with the term BTL commonly used in hospital settings. Tubal ligation can be either unilateral or bilateral. However, for effective prevention of pregnancy, it is important for both fallopian tubes to be blocked or sealed.
Bilateral tubal ligation procedure (BTL): How is it done?
BTL can be performed through two methods:
Minilaparotomy:
- This involves a small (usually less than 5 cm) suprapubic incision into the pelvic cavity.
Laparoscopy:
- This technique involves performing the operation in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera known as a laparoscope.
BTL is considered a relatively minor surgery, and many women can typically return home on the same day of the procedure.
How effective is BTL in preventing pregnancy?
Laparoscopic sterilisation is more than 99% effective at preventing pregnancy.
Who needs BTL?
BTL is suitable for:
Women who want a permanent method of contraception.
Women at risk of medical complications from future pregnancies, for instance, women with conditions such as high-risk heart disease.
Who is not suitable for BTL?
BTL should not be considered if you:
are uncertain or have mixed feelings about the procedure
are younger than 30 years, as they are statistically more likely to experience regret following the procedure compared to older women
are incapable of making a medical decision,
are diagnosed with gynecological malignancies, as sterilisation may not be the primary concern in the presence of such medical conditions.
desire for future childbearing
What are the pros and cons of BTL?
Pros of BTL
High effectiveness:
BTL is more than 99% effective at preventing pregnancy, providing a reliable form of contraception.
Hormone levels remain unaffected:
It does not impact hormone levels, thus it will not interfere with your menstruation cycle.
Immediate effectiveness:
- BTL is typically effective immediately, although it's advisable to use contraception until the next menstrual cycle.
No impact on sex drive:
It does not affect sex drive or interfere with sexual function.
Cons of BTL
No protection against STIs:
- BTL does not protect against STIs, emphasising the importance of using barrier methods (eg: condoms) if protection against STDs is needed.
Irreversible nature:
- The procedure is basically irreversible, making it crucial for individuals to be certain about their decision.
Rare but possible failure:
BTL can fail, although it is rare, and if pregnancy occurs after the procedure, there’s an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
How much does BTL cost in Singapore?
The cost of BTL in Singapore depends on the type of procedure, the type of hospital you choose (public or private), and the doctor’s fees. However, referring to the Ministry of Health's (MOH) fee benchmarks, the cost for this procedure ranges from as low as around $2,000 to as high as $15,000.
What are the side effects of having a BTL?
Mortality is low (about 0.01% to 0.02%) and mostly related to general anesthesia. The risks of the surgery includes:
Risk of injury:
Potential risks include injury to the bowel, bladder, or blood vessels during the surgery.
Failure to achieve sterility:
While rare, there is a possibility of the procedure not achieving the intended sterility.
Pain:
- Post-operative pain is a common concern, though it is typically managed with appropriate pain relief measures.
Infection:
- As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection, which is typically minimised through sterile techniques.
FAQ
What are the side effects of bilateral tubal ligation (BTL) after c-section?
There are no differences in the side effects between undergoing BTL independently and having it performed after c-section.
Is bilateral tubal ligation (BTL) 100% effective?
BTL is not 100% effective at preventing pregnancy. In fact, there is no single contraception method that is considered 100% effective. Although BTL is considered a permanent contraception, pregnancy can still occur in 1 out of 200 cases.
What are some alternatives to bilateral tubal ligation (BTL)?
Long-acting reversible contraception methods such as the intrauterine device (IUD) or birth control implant (Implanon) can last for several years and are about as effective at preventing pregnancy as BTL. They can be removed anytime if you want to become pregnant. Another alternative is having a vasectomy, a method of male sterilisation for your partner.
Vasectomy VS tubal ligation: Is it better to get a vasectomy or tubes tied?
| Vasectomy | Tubal Ligation | |
| Procedure | Cutting or sealing the vas deferens of males | Blocking, sealing, or cutting fallopian tubes of females |
| Effectiveness | Highly effective at preventing pregnancy | Highly effective at preventing pregnancy |
| Reversibility | Reversal is possible but not always successful | Reversal is possible but more complex and success rates vary |
| Procedure time | Generally quicker recovery time | May have a slightly longer recovery time |
| Invasiveness | Generally considered less invasive | Slightly more invasive |
| Permanent nature | Permanent, reversal is not guaranteed | Permanent, reversal is not guaranteed |
The decision between getting a vasectomy or having tubal ligation (tubes tied) is highly personal and depends on various factors. There is no universal solution, as what may be "better" for one individual or couple may not be the same for another.
What to expect after bilateral tubal ligation (BTL)?
After surgery, you will be observed for some time to ensure there are no problems or complications post-operatively. Most women can go home on the same day after the procedure, though you will need someone to take you home. You may feel some discomfort or have other symptoms that last a few days:
Dizziness and nausea
Abdominal cramps
Gassy or bloated feeling
Sore throat (from the breathing tube if general anesthesia was used)
Most women return to their normal routines within one week of surgery.
Does bilateral tubal ligation (BTL) stop periods?
No, BTL will not affect your hormone levels, thus will not interfere with your menstruation.
Bilateral tubal ligation (BTL) reversal: What if I decide I want to get pregnant after I have the procedure?
If you opt for BTL but later change your mind after the operation, attempting to reverse the procedure may not always be successful. Many women may still find it difficult to become pregnant even after a reversal is done. Additionally, in cases of post-BTL pregnancies, there is an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy, further emphasising the importance of careful consideration and consultation before choosing this permanent contraceptive method.
References
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists 2022
Date SV, Rokade J, Mule V, Dandapannavar S. Female sterilization failure: Review over a decade and its clinicopathological correlation. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2014 Jul;4(2):81-5. doi: 10.4103/2229-516X.136781. PMID: 25143881; PMCID: PMC4137647.
Marino S, Canela CD, Nama N. Tubal Sterilization. [Updated 2022 Sep 5]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Novena:
6592 6686 (Call), 8611 8986 (WA) - Bukit Batok:
6569 0668 (Call), 8686 3525 (WA) - Choa Chu Kang:
6893 1227 (Call), 8282 1796 (WA) - Jurong:
6262 8588 (Call), 6262 8588 (WA) - Katong (female doctor):
6970 2272 (Call), 8611 9020 (WA) - Punggol:
6243 6843 (Call), 8811 0328 (WA) - Sembawang: 6753 5228
- Sengkang: 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): 6382 3313
- Tampines: 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: 6276 1525
Notice
The range of services may vary between TWC/TS locations. Please contact your preferred branch directly to enquire about the current availability.
Request an AppointmentDr Ryan Lee Wai Kheong
Obstetrics & Gynaecology (O&G)
Thomson Specialists Woodleigh (Women's Health)
English, Mandarin
Prudential, Great Eastern, Adept, MHC and 4 others

