Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) but often shows no symptoms. This means that many people with the infection are unaware that they have it. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications affecting your fertility and overall health. However, the good news is that chlamydia can easily be detected through a screening test and is completely curable with antibiotics.
Getting tested is the best way to protect your sexual health and prevent passing the infection to others. Whether you're experiencing symptoms or simply want a routine check, understanding how and where to test is an important step in taking care of yourself.
What is chlamydia?
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by bacteria called Chlamydia trachomatis. It spreads through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. You may have heard the term sexually transmitted disease (STD) before. While often used interchangeably, STI is more accurate because you can have an infection without showing symptoms.
Many chlamydia infections show no symptoms, so people often don’t know they’re infected. If left untreated, it can cause serious complications. In women, it may lead to pelvic inflammatory disease or PID (an infection of the reproductive organs, including the fallopian tubes), infertility, or ectopic pregnancy. Men can experience inflammation of the testicles and fertility problems.
Although this may sound worrying, chlamydia is curable. With testing and proper treatment, most people recover fully without lasting effects.
What are symptoms of chlamydia?
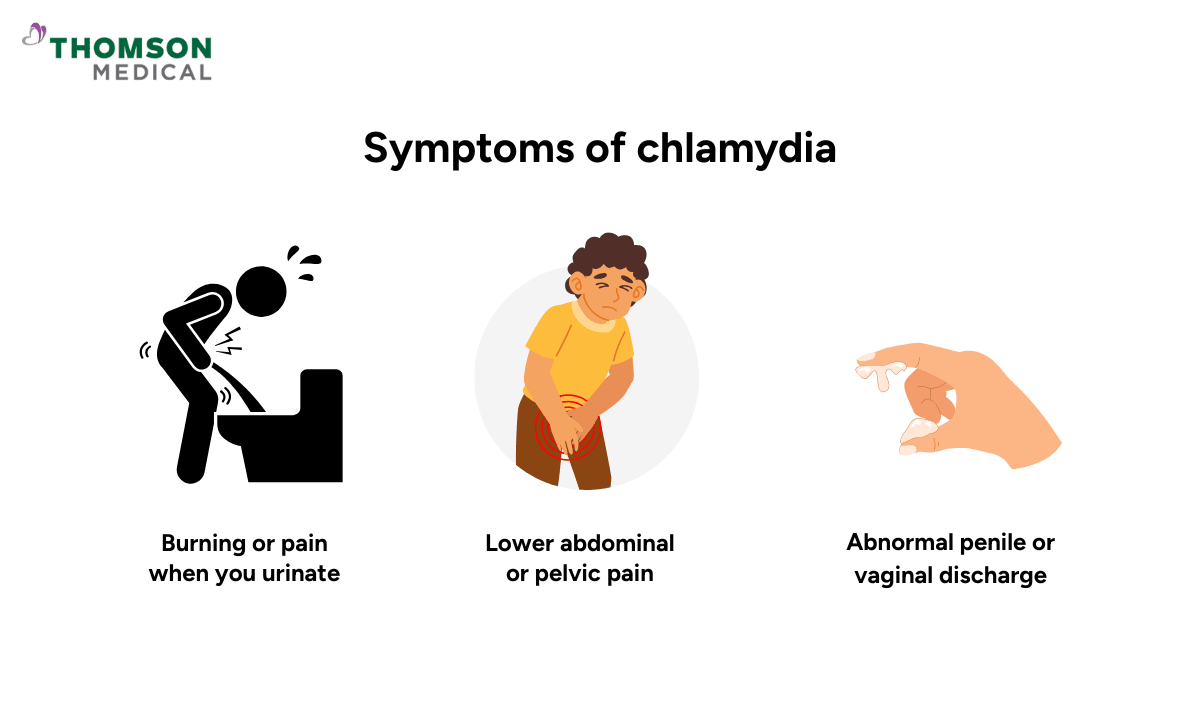
Chlamydia is sometimes called a “silent” infection because it may not show obvious signs. When symptoms appear, they often start one to three weeks after exposure. Common signs include:
Burning or pain when you urinate
Abnormal penile or vaginal discharge
Pain during intercourse, especially for women
Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
Bleeding between periods or after intercourse (in women)
Swollen testicles (in men)
Because symptoms can be mild, regular screening matters, especially if you have new or multiple partners. Detecting chlamydia early prevents complications and stops the infection from spreading.
Why does chlamydia testing matter?
Chlamydia often causes no symptoms at all, which means you could be infected without knowing it. You might feel completely well while the bacteria continue to spread and cause harm to your reproductive system.
Regular testing is the only reliable way to know if you have chlamydia. Early detection means:
Start treatment immediately before complications develop
Avoid passing the infection to your partners
Prevent long-term problems such as infertility or PID
Even if you don't have symptoms, getting tested is important, especially if you've had unprotected sex, new or multiple partners, or if your partner has been diagnosed with an STI.
Where to get tested for chlamydia in Singapore?
Testing for chlamydia in Singapore is straightforward, confidential, and available at many clinics. You can visit:
General practitioner (GP) clinics
Polyclinics
Private sexual health clinics
Hospitals and specialist centres
STD screening facilities
Your doctor will recommend the right test based on your symptoms and situation. Testing involves either a urine sample or a swab from the area where the infection may be present.
Our STI/D specialists
Loading...
What test method is used for chlamydia?
The most accurate test for chlamydia is the PCR test (Polymerase Chain Reaction), which is a type of NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Test). This test looks for the bacteria's genetic material (DNA) in your sample, even when you don't have symptoms.
Unlike older tests that look for antibodies or try to grow the bacteria in a lab, PCR directly detects the chlamydia bacteria itself. This makes it highly accurate and reliable. Most clinics and hospitals in Singapore use PCR testing as the standard method for diagnosing chlamydia.
How is the sample collected?
Your doctor will choose the sample type based on your symptoms and sexual history. The PCR test can be performed on different types of samples, and no blood test is needed because chlamydia is detected directly from urine or swabs, not from the blood.
Urine test
This is the simplest option for both men and women. You provide a urine sample, and the laboratory runs the PCR test on it. No physical exam needed.
Swab test
For women, your doctor may take a vaginal swab or sample from the cervix (the opening to your womb). For men, a swab from the urethra (the tube where urine comes out) may be used. If you've had anal intercourse, rectal swabs can detect infection in that area, and if you've had oral intercourse, throat swabs can detect the infection.
All these samples are tested using the same PCR method. The results are available in a few days.
Early testing and treatment help prevent long-term problems and stop the infection from spreading to others. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical to get tested and receive tailored guidance on next steps for your sexual health.
How much does chlamydia testing cost in Singapore?
The cost of a chlamydia test varies depending on where you go and which test you choose.
At public clinics, a chlamydia PCR test costs around SGD 60 to 70 per test site. These rates are subsidised for Singapore residents and permanent residents.
At private clinics or hospitals, prices can range from SGD 150 to 200 or more. The final cost depends on:
The test method used
How many sites are tested (urine, vaginal, rectal, throat)
Whether you're getting a package that screens for multiple infections
Consultation fees
Unfortunately, routine chlamydia testing is not covered by Medisave in Singapore. Community Health Assist Scheme (CHAS) subsidies may be available at some clinics, though coverage varies depending on your CHAS card type and the specific clinic. However, some private health insurance plans may provide coverage, depending on your policy. To further reduce costs, some healthcare facilities in Singapore may offer subsidised or affordable tests.
Prices mentioned are estimates and may vary. For a personalised price estimate, information on payment options, subsidies, and insurance coverage, contact our medical concierge.
How is chlamydia treated?
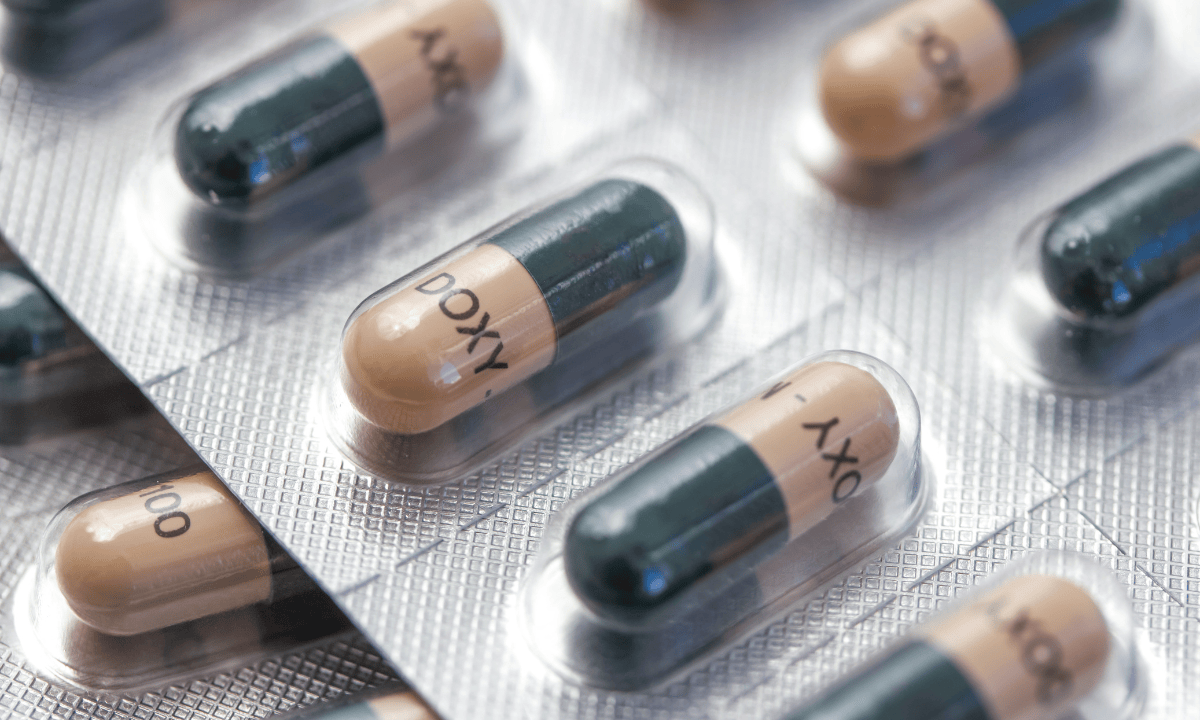
Chlamydia is easily cured with antibiotics. Most people receive doxycycline 100 mg, taken twice daily for seven days. In some cases, you might receive azithromycin 1 g as a single dose instead.
If you're pregnant, doxycycline isn't suitable. Your doctor will prescribe azithromycin or amoxicillin instead. You'll also need a follow-up test 3 to 4 weeks after treatment to confirm the infection has cleared.
Most people feel better in a few days. If your symptoms continue, follow up with your doctor.
How long does it take to cure chlamydia?
Once you start antibiotics, most infections clear within seven days.
If you take a single dose of azithromycin, avoid all sexual contact for at least seven days after taking it.
If you take doxycycline, wait until you've finished the full seven-day course before having sexual contact again.
A follow-up test isn't needed unless:
Your symptoms don't go away
You didn't complete your treatment
There's a chance you were exposed again
However, doctors recommend retesting three months later to confirm you haven't been reinfected since treatment.
If you’ve been diagnosed with chlamydia or want to ensure effective treatment, request an appointment with Thomson Medical. Our specialists can guide you to the right treatment, advise on safe timing for sexual activity, and provide follow-up care to prevent reinfection.
How to prevent chlamydia
Chlamydia is preventable with a few simple habits. Here's how you can protect yourself and your partner:
Use condoms or dental dams consistently during intercourse
Limit sexual partners and know their STI status
Get tested regularly, especially if you're under 25 or have new partners
Avoid an intercourse with anyone showing infection symptoms
Ensure both partners are tested and treated if needed
Regular check-ups help detect infections early and reduce the risk of spreading STIs. Open communication with your partner is also key to maintaining sexual health.
FAQ
Which test confirms chlamydia?
The NAAT (also called PCR) test is the gold standard. It detects the bacteria's DNA using either a urine sample or a swab from the affected area.
Can I test myself for chlamydia?
In Singapore, home test kits aren't commonly available or officially approved. Some clinics offer self-collection options where you take your own sample, but visiting a clinic for testing remains the most reliable and confidential method.
Can I get a chlamydia test at a pharmacy?
Pharmacies in Singapore don't conduct STI tests. You'll need to visit a clinic or diagnostic lab for testing.
Is chlamydia common in Singapore?
Yes. Chlamydia is one of the most frequently reported STIs in Singapore, particularly among young adults under 25. Regular sexual health screening helps detect it early, even when you have no symptoms.
Who is at higher risk for chlamydia?
Anyone sexually active can get chlamydia. Risk increases if you're under 25, have multiple sexual partners, don't use condoms consistently, or skip routine STI screenings.
Is chlamydia curable?
Yes, absolutely. Chlamydia is completely curable with antibiotics. However, you can get reinfected if you're exposed again. Make sure your partner is also treated, and practise safe sex to prevent future infections.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice, please consult a specialist at Thomson Medical. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Novena:
6592 6686 (Call), 8611 8986 (WA) - Bukit Batok:
6569 0668 (Call), 8686 3525 (WA) - Choa Chu Kang:
6893 1227 (Call), 8282 1796 (WA) Jurong:
6262 8588 (Call), 6262 8588 (WA)- Katong (female doctor):
6970 2272 (Call), 8611 9020 (WA) - Punggol:
6243 6843 (Call), 8811 0328 (WA) - Sembawang: 6753 5228
- Sengkang: 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): 6382 3313
- Tampines: 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: 6276 1525
