Sexual education topics such as safe sex and STD vaccinations are often considered taboo. Whenever these topics are discussed, some people may feel uncomfortable or embarrassed, which makes STD prevention difficult. The reality is that STDs are more common than many people realize and they can affect anyone who is sexually active.
However, you shouldn't feel embarrassed or worried about being judged for taking steps to prevent STDs; it's a responsible choice that shows you care about your health and your loved ones.
What are STDs?
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections passed through sexual contact. You might also hear them called Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI). Both terms mean the same thing and are used interchangeably. Bacteria, viruses, or parasites cause these infections, and they can affect anyone. While many STDs don't show symptoms for months or even years, which is why prevention and regular testing matter.
What causes STDs?
Three main types of germs cause STDs. Bacteria cause infections like chlamydia, gonorrhoea, and syphilis. These can be cured with antibiotics when caught early. Viruses cause human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), herpes, human papillomavirus (HPV), and hepatitis. While the STD infections caused by viruses can't be fully cured, they can be managed with treatment. Parasites cause trichomoniasis, which specific medications can treat effectively.
How can you prevent STDs?
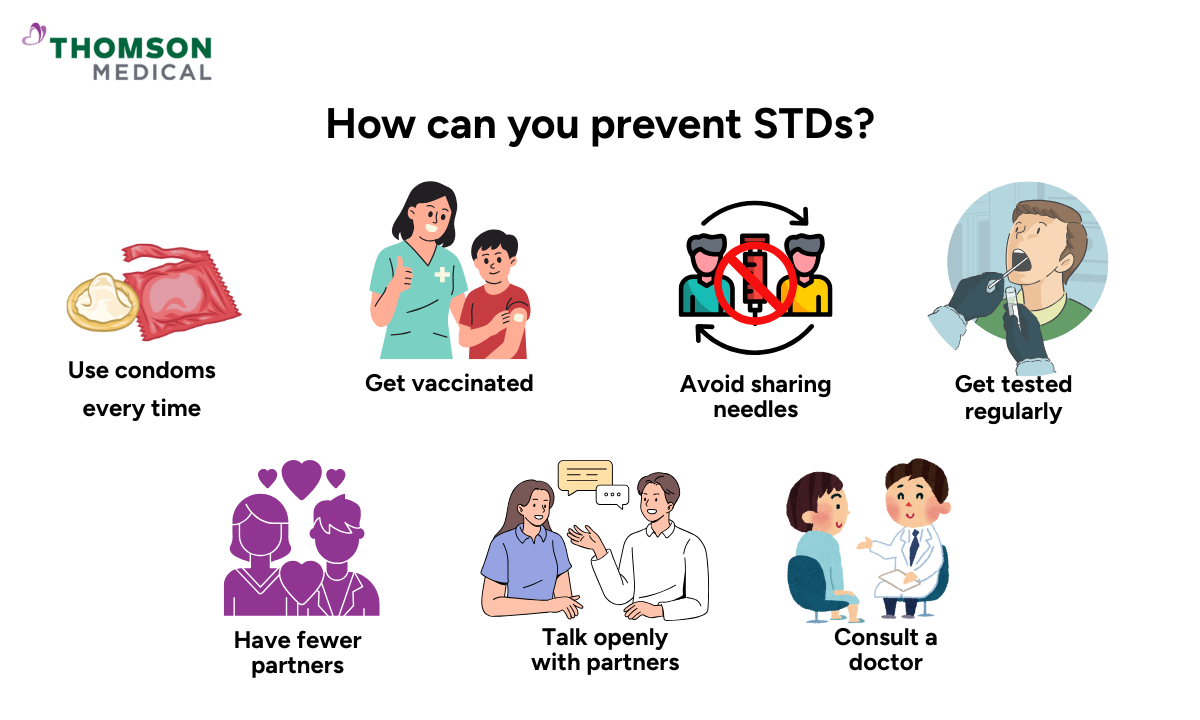
Taking simple steps to protect yourself shows you care about your health and those close to you. Here's what works:
Use condoms every time
Condoms block many STDs, including HIV, bacterial infections like chlamydia, gonorrhoea, and syphilis, when used correctly. While they don't fully protect against skin-to-skin infections like herpes or HPV, they remain one of your strongest defenses. If you're allergic to latex, polyurethane condoms offer the same protection and work with both oil-based and water-based lubricants.
Get vaccinated
Singapore offers HPV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis A vaccines that prevent infections with serious long-term effects. HPV vaccines protect against the virus that causes cervical cancer and genital warts. Hepatitis B and A vaccines protect your liver from viruses that can spread through sexual contact. These vaccines are available at various public or private hospitals, polyclinics or clinics.
There are currently no vaccines for chlamydia, gonorrhoea, or syphilis, which makes safer sex and regular testing especially important.
Avoid sharing needles
Using shared needles for drugs, steroid injections, or even unregulated beauty treatments can spread HIV and hepatitis. Always use sterile equipment and never share. Piercings and tattoos are safe when done at licensed studios that use sterile, single-use needles and proper hygiene practices.
Get tested regularly
Testing detects infections before symptoms appear, which means faster treatment and less chance of passing them to someone else. If you're sexually active, annual testing is recommended. If you have multiple partners, test every 3-6 months.
Have fewer partners
Limiting your number of sexual partners reduces your risk of exposure to STIs. The fewer partners you have, the lower your chances of encountering an infection.
Talk openly with partners
Being honest about testing history and sexual health makes a real difference. These conversations might feel awkward at first, but they protect both of you. Discuss your STI status, when you were last tested, and whether you're seeing other people. These conversations might feel uncomfortable at first, but they're a normal part of responsible sexual health.
Consult a doctor
A doctor can assess your personal risk factors and recommend the right prevention actions for your situation. They can advise on vaccines you may need, suggest appropriate testing schedules, or discuss options like PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis), a daily medication that prevents HIV infection.
Our specialists
Loading...
What are the STD symptoms?
Many people with STDs show no symptoms at all, which is why testing matters even when you feel fine. When symptoms do appear, you might:
Notice pain or burning sensation when urinating
Unusual discharge for penis or vagina
Sores, blisters or bumps in the genital area
Itching, or irritation around the genitals
Discomfort during sex
Swollen lymph nodes in your groin (top of your thigh meets your lower abdomen)
Some infections stay hidden but can still affect you and your partner. Getting tested regularly is a caring way to look after your health and theirs.
When do I need an STD test?
If you notice any symptoms that concern you, get tested even if they seem minor. STD testing is especially important if you're:
Sexually active
Not using condoms consistently
Having multiple partners or starting a new relationship
Noticing symptoms
Planning to pregnant
Your doctor isn’t there to judge, they’re there to help you stay safe and healthy. You don’t always need to wait for your next routine check-up. Sometimes, it’s important to reach out for care right away, whether that means talking to a doctor or getting tested.
If you are concerned about your sexual health or have experienced any symptoms, schedule an appointment with Thomson Women’s Clinic. Depending on your needs, our specialist can recommend relevant tests or vaccination services. All consultations are conducted in a confidential and professional setting, with sensitivity to your concerns.
Where can you get tested?
In Singapore, STD tests are widely available and can be carried out at various public or private hospitals, polyclinics or clinics.
The cost can vary depending on the type of test and whether it is performed at a public or private facility. However, in general, STD test prices in Singapore are as follows:
Basic STD tests such as chlamydia and gonorrhoea can cost between SGD 50 and SGD 150 per test.
HPV and Pap smear tests can cost between SGD 100 and 250.
More comprehensive STD screening (covering multiple infections such as HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis) can range from SGD 150 to SGD 500 or more, depending on the scope of the tests.
HIV testing can range from SGD 50 to 100 for a standard test, although some clinics offer free HIV testing.
Unfortunately, STD testing is not covered by Medisave or the Community Health Assist Scheme (CHAS) in Singapore. However, some private health insurance plans may provide coverage, depending on the policy. To further reduce costs, some healthcare facilities in Singapore may offer subsidised or affordable tests.
FAQ
What are 5 ways to prevent STDs?
Consistent condom use, HPV and Hepatitis B vaccination, regular testing without waiting for symptoms, limiting sexual partners, and honest conversations about sexual health with partners.
Do condoms prevent STDs?
They work well against HIV, chlamydia, and gonorrhoea. However, herpes and HPV present challenges because they spread through skin-to-skin contact beyond what condoms cover. Despite this limitation, condoms stay among your most effective protective options.
What to do if my partner has an STD?
Get tested regardless of symptoms. Many infections hide without obvious signs. Follow your doctor's treatment recommendations completely. Condoms become non-negotiable until both partners finish treatment and receive medical clearance. Previous partners need notification so they can seek testing too.
What STDs are not curable?
HIV, herpes, hepatitis B and certain strains of HPV can remain in the body for long periods of time. However, antiviral medications can effectively manage these conditions. Antiretroviral therapy keeps HIV under control, antiviral medications reduce herpes outbreaks and antiviral drugs help to manage chronic hepatitis B.
For HPV, although there is no cure, most infections clear up naturally within two years and vaccines can prevent infection with high-risk strains.
How soon can you pass on an STD?
Transmission happens fast. HIV moves to new hosts shortly after initial infection. Herpes transfers even without visible sores through viral shedding. Chlamydia and Gonorrhea spread immediately, typically before the infected person notices anything wrong.
How to deal with an STD?
Begin treatment right away. Your partners deserve notification so they can get tested and treated if needed. Complete every dose of prescribed medication, even after symptoms disappear. Attend all follow-up appointments your doctor schedules. Condoms remain essential going forward.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice based on your unique situations, please consult a specialist at Thomson Medical.Request an appointment with Thomson Medical today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Novena:
6592 6686 (Call), 8611 8986 (WA) - Bukit Batok:
6569 0668 (Call), 8686 3525 (WA) - Choa Chu Kang:
6893 1227 (Call), 8282 1796 (WA) Jurong:
6262 8588 (Call), 6262 8588 (WA)- Katong (female doctor):
6970 2272 (Call), 8611 9020 (WA) - Punggol:
6243 6843 (Call), 8811 0328 (WA) - Sembawang: 6753 5228
- Sengkang: 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): 6382 3313
- Tampines: 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: 6276 1525
