Experiencing persistent back pain, numbness, or tingling that won’t go away? You might be dealing with a slipped or herniated disc—a common spinal condition that affects many people, especially those with physically demanding jobs or sedentary lifestyles. When symptoms become troubling or unclear, doctors often recommend an MRI scan to get a detailed look at what’s happening inside your spine.
What is a lumbar herniated disc MRI?
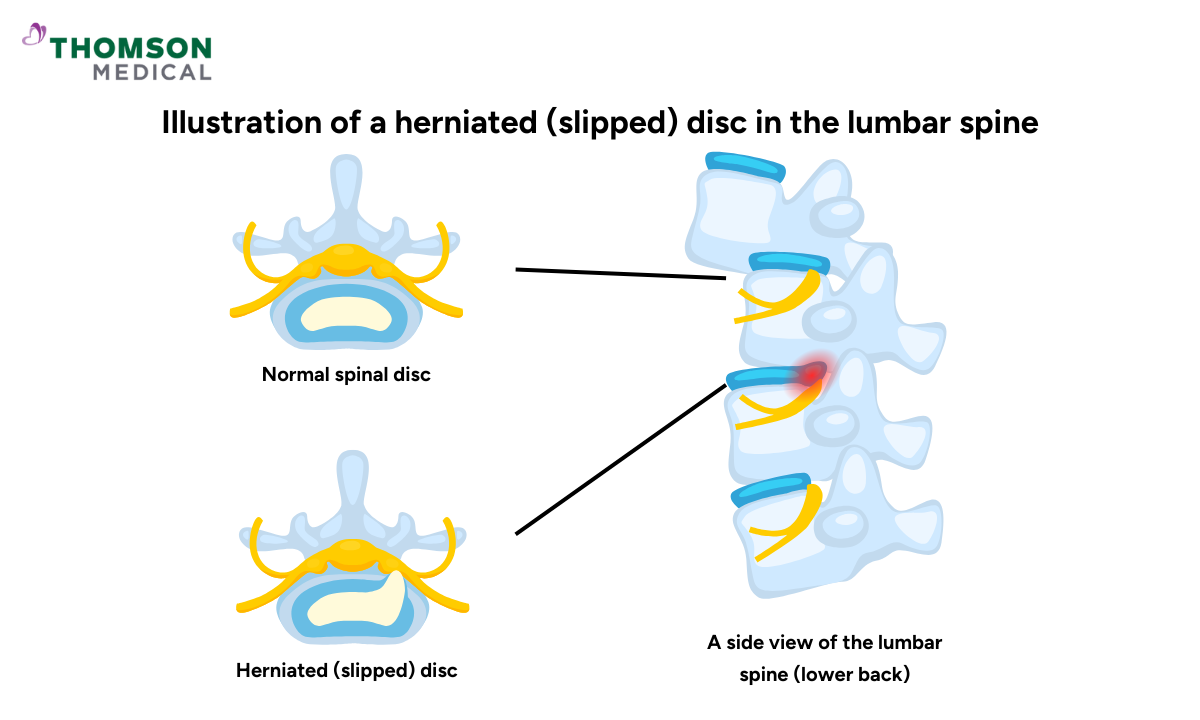
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or bulging disc, occurs when the soft inner part of an intervertebral disc pushes through a crack in its tough outer layer, called the annulus fibrosus. This can press on nearby nerves or into the spinal canal, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness—especially in the back, neck, arms, or legs.
This condition most commonly affects the lumbar spine (lower back) but can also occur in the cervical or thoracic spine. Common causes include ageing, wear and tear, or sudden injuries.
An MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging) scan for a lumbar herniated disc is a safe, non-invasive test that uses strong magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images of the spine. It helps doctors pinpoint the exact location of the herniated disc and assess whether any spinal nerves are being compressed.
In addition to identifying herniated discs, MRI can detect related conditions such as bulging discs and annular tears, which may contribute to back pain or nerve symptoms. This imaging is important for accurate diagnosis and planning the right treatment.
When do you need an MRI for a lumbar herniated disc?
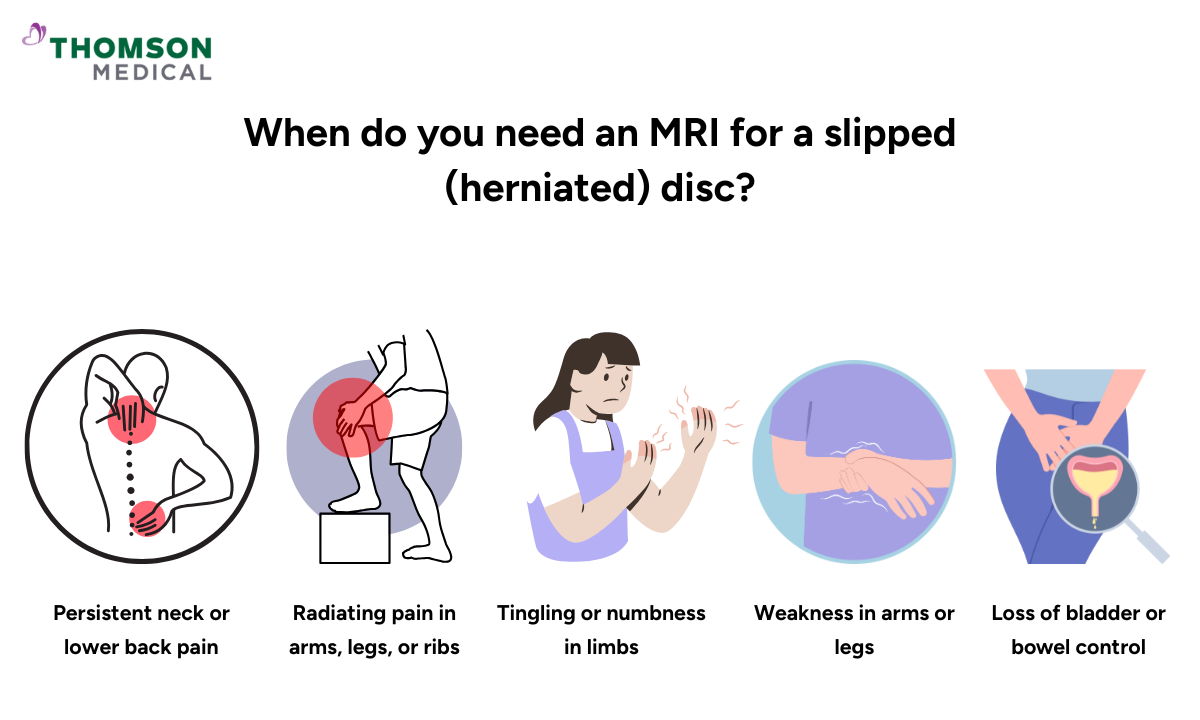
Your doctor may recommend a spine MRI scan if you’re experiencing symptoms that suggest a herniated (slipped) disc. These common symptoms often vary depending on where in the spine the disc is affected, but common signs include:
Persistent neck or lower back pain
Sharp or radiating pain that travels down the arms, legs, or around the ribs
Tingling, numbness, or a “pins and needles” feeling in the arms or legs
Muscle weakness in the limbs
Difficulty controlling your bladder or bowel movements (a serious symptom that may indicate nerve compression and requires urgent medical attention)
Therefore, an MRI helps confirm whether a herniated disc is the cause of your symptoms and shows exactly where the disc is pressing on nerves.
If you are experiencing symptoms suggestive of a slipped (herniated) disc, such as persistent back pain or nerve-related discomfort, request an appointment with us to assess whether an MRI scan is appropriate for your condition.
How to prepare for a lumbar herniated disc MRI?
Preparation for an MRI scan may vary depending on the testing facility, so it’s best to consult your healthcare provider before doing the scan.
Prior to the scan, your doctor will typically conduct a physical examination and review your medical history. Be sure to inform your doctor if you:
Have any existing medical conditions
Are taking medications, or supplements, or have allergies to any medication
Have any implanted medical devices, such as pacemakers or metal implants
Are pregnant or breastfeeding, as MRI contrast dyes may not be recommended in these cases
Feel anxious in small or enclosed spaces (claustrophobia), as your doctor may prescribe a mild sedative to help you relax
How does the MRI for a slipped (herniated) disc work?
MRI for a herniated disc can clearly show the spinal cord, vertebrae, discs, and surrounding soft tissues. Moreover, this imaging helps detect:
The location and severity of a herniated disc
Spinal alignment issues
Inflammation of nerves or the spinal cord
Damage caused by injury
Other possible causes of back pain
As a result, an MRI provides a clear and accurate view of the spine, making it a valuable tool for diagnosing slipped discs and planning appropriate treatment.
How to read an MRI for a lumbar herniated disc?
Reading an MRI for a lumbar herniated disc starts with understanding what a normal spine looks like. On an MRI scan, the lumbar spine (lower back) shows a series of bones (vertebrae) separated by soft, cushion-like intervertebral discs, along with nearby structures like facet joints and nerve roots. Here’s how to spot a herniated disc:
Look at the discs between the lower back bones (usually L4–L5 or L5–S1):
On a healthy scan, discs appear smooth and evenly spaced.
Check for bulging or protrusion:
If part of a disc is sticking out beyond its usual boundary, it may be herniated.
T2-weighted images help most:
Herniated discs often press on the nerves and may show up as darkened or uneven areas.
Look for nerve root compression:
If the disc is touching or pressing on a nerve, you may see narrowing in the spinal canal or nerve passage (foramen).
Other signs:
Swelling, inflammation, or reduced disc height may also point to a disc problem.
Risks and side effects of a lumbar herniated disc MRI
MRI scans for slipped (herniated) discs are generally safe and widely used. However, there are a few potential risks and side effects to be aware of:
Loud noises from the MRI machine, which may cause discomfort (ear protection is usually provided)
Allergic reactions to contrast dye (if used), such as nausea, dizziness, flushed skin, or hives – though this is rare
Claustrophobia, or discomfort from lying in an enclosed space for a prolonged period
Stress or anxiety, especially if you're nervous about medical procedures or the scan results
Always let your doctor know if you have allergies, implants, or a fear of confined spaces, so they can make adjustments to ensure your comfort and safety.
The cost of a lumbar herniated disc MRI scan in Singapore
The cost of an MRI scan for a slipped disc in Singapore depends on several factors, including the region of the spine affected (typically the lumbar spine), whether contrast dye is required, the inclusion of specialist consultations, and whether the scan is done in a public or private healthcare facility.
At subsidised rates in public hospitals, a slipped disc MRI scan generally costs between SGD 300 and SGD 800, depending on the scan's complexity and whether it involves the lumbar or cervical spine. Patients without subsidies or referrals may incur higher charges. Non-subsidised rates may go above SGD 1,000.
In private hospitals or imaging centres, the cost can range from SGD 900 to over SGD 2,000, especially if a contrast-enhanced MRI or consultation with a spine specialist is required.
Factors that may affect the total cost include:
Whether the slipped disc is in the lumbar or cervical spine
Use of contrast dye for enhanced imaging clarity
Specialist consultation or follow-up required before or after the scan
Choice of public versus private healthcare provider
The information provided above is intended for general reference only. For detailed fee information and payment options, please consult your healthcare provider directly. Request an appointment with our specialists at Thomson Medical for a detailed price breakdown and a personalised care plan.
FAQ
What causes a herniated disc?
A herniated disc happens when the nucleus pulposus—the soft, jelly-like centre of a spinal disc—pushes out through a tear in the annulus fibrosus, the tough outer layer made up of strong outer fibres. These fibres help contain the inner material, but over time they can weaken due to ageing, repeated strain, or sudden injury (like lifting something heavy or twisting the spine). As the disc loses moisture and flexibility with age (a condition known as degenerative disc disease), it becomes more likely to tear and lead to a herniation.
Does an MRI show a slipped disc?
Yes, an MRI scan can clearly show a herniated disc. It helps detect the presence, disc pain location, and severity of the herniated discor disc injuries and shows whether any nearby spinal nerves are being compressed. MRI also provides detailed images of the soft tissues in your spine, making it the best scan for identifying disc problems and planning appropriate disc treatment.
What is the best scan for a slipped disc?
The best scan for detecting a slipped disc is an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). It provides clear and detailed images of the spinal discs, nerves, and soft tissues, making it highly effective for identifying disc herniation, nerve compression, and the severity of the condition. MRI is non-invasive and does not involve radiation, making it a safe and accurate choice for diagnosing spine problems.
How serious is a slipped disc?
A slipped disc can range from mild discomfort to severe pain that affects your daily activities. In more serious cases, it may press on spinal nerves and cause symptoms such as numbness, weakness, or even loss of bladder and bowel control (incontinence), which requires urgent medical attention.
What are the four stages of a slipped disc?
The four stages of a slipped disc show how the disc gets worse over time:
Disc bulge: The disc starts to push out slightly, but nothing has torn.
Protrusion: The soft inside of the disc pushes harder and creates a bigger bump, but it’s still held in place.
Extrusion: The soft part breaks through the outer layer but is still attached.
Sequestration: The soft part breaks off completely and may move into the space near the spinal nerves.
Is a herniated disc and a slipped disc the same?
Yes, a herniated disc and a slipped disc refer to the same condition. Both terms describe a situation where the soft inner part of a spinal disc pushes out through a tear or weakness in the outer layer. This condition can press on nearby nerves and cause symptoms like pain, numbness, or weakness. “Slipped disc” is a more commonly used term, while “herniated disc” is the more accurate medical term.
Can an MRI tell how old a herniated disc is?
An MRI can give clues about whether a herniated disc is recent or old, but it cannot tell the exact age. Changes in fluid and disc condition may suggest how long it has been there.
How to fix a slipped disc?
There are several treatment options for a slipped disc, depending on how serious it is. In more severe cases, doctors may recommend one of the following procedures:
Spinal fusion surgery:
This joins two or more bones in the spine together to stop movement and reduce pain.
Discectomy:
This removes the part of the disc that is pressing on a nerve to relieve pain and pressure.
Microdiscectomy:
A more precise version of discectomy using smaller cuts to remove the disc material and reduce nerve pressure.
Artificial disc replacement:
The damaged disc is fully removed and replaced with a man-made disc to keep the spine flexible.
Your doctor will decide the best spinal surgery options based on your symptoms, age, and overall health.
What are disc levels in a lumbar spine MRI?
Disc levels refer to the spaces between the bones in your lower back (lumbar spine) where the spinal discs sit—such as L4–L5 or L5–S1. These levels are important in MRI scans because they are common sites where a herniated or bulging disc can press on nearby spinal nerves, causing pain or numbness.
Why are disc levels important when diagnosing a slipped disc?
Most nerve root compression happens at the disc level, making it a key area doctors check during an MRI. Identifying which disc level is affected helps guide the diagnosis and treatment plan for conditions like a slipped disc or sciatica.
Can MRI show nerve damage?
Yes, an MRI can show signs of nerve damage. It provides detailed images of the nervous system and can reveal changes such as nerve compression, inflammation, or shrinkage, as well as damage to the surrounding tissues. This information helps doctors identify the cause of symptoms like pain, numbness, or weakness.
How long does a slipped disc take to heal?
Most slipped discs improve within 6 to 8 weeks with rest, physiotherapy, and pain management. However, recovery time can vary depending on the severity and individual health condition. Some cases may take longer or require medical procedures.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice, please consult a specialist at Thomson Medical. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Medical Concierge
- 8.30am - 5.30pm
- WhatsApp: 9147 2051
Need help finding the right specialist or booking for a group?
Our Medical Concierge is here to help you. Simply fill in our form, and we'll check and connect you with the right specialist promptly.
Notice:
The range of services may vary between Thomson clinic locations. Please contact your preferred branch directly to enquire about the current availability.
Get In Touch