Have you recently undergone intrauterine insemination (IUI) treatment? Following the procedure, your fertility specialist may recommend taking progesterone supplements to help ensure conception. But what exactly does progesterone do, and is it necessary for a successful pregnancy?
To help you better understand how progesterone affects your chances of conception, let's start by looking at what this hormone is.
What is progesterone?
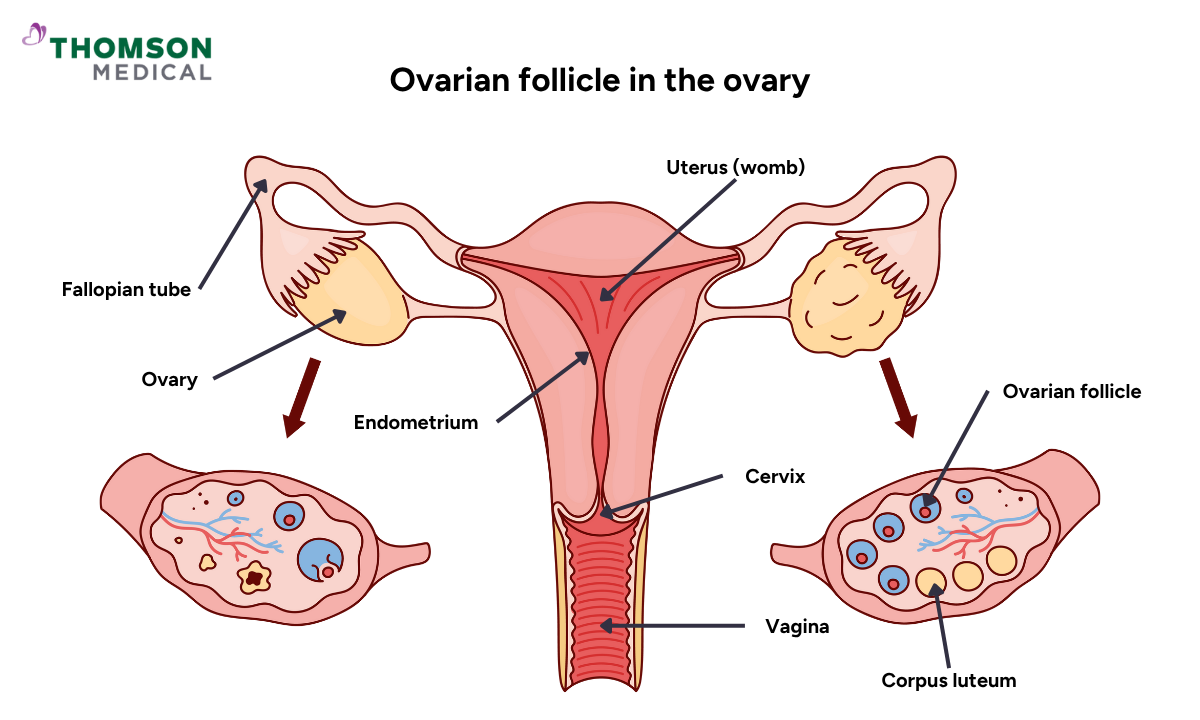
Progesterone is a natural hormone produced by the corpus luteum, which is the remains of an ovarian follicle after releasing its egg during ovulation. This hormone makes pregnancy possible by thickening the endometrium (uterine lining), which helps a fertilised egg implant itself in your womb and grow into a foetus.
During natural conception, when an egg is fertilised, the progesterone hormone signals the womb to prepare for pregnancy, which prevents the menstrual cycle from occurring.
However, depending on your fertility conditions, you may not produce enough progesterone to sustain an early pregnancy. Your fertility specialists may recommend taking progesterone supplements to sustain an early pregnancy after fertility treatments like IUI.
These medications contain the same properties as natural progesterone and increase the likelihood of conception while supporting the luteal phase (the time between ovulation and your next period).
If pregnancy does not occur, your progesterone levels will drop naturally, the uterine lining will shed, and your period will start.
Why are progesterone supplements recommended after an IUI treatment?
After an IUI procedure, progesterone supplementation can help create the optimal environment for a successful early pregnancy. This hormonal medication is often recommended after IUI for the following reasons:
Reduces uterine contractions that could disrupt implantation.
Maintaining and thickening the uterine lining helps the fertilised egg implant itself.
Prolongs the luteal phase in women with certain hormonal disorders, including polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or irregular cycles.
Prevents low progesterone levels, thereby prolonging the lifespan of the uterine lining and maintaining the early stages of pregnancy.
Supports early pregnancy until the placenta produces sufficient amounts of progesterone and takes over the hormone production from the corpus luteum.
When should I take progesterone supplements after IUI?
Since the corpus luteum produces natural progesterone before the placenta takes over later in pregnancy, you might not always require progesterone treatment after an intrauterine insemination.
However, your doctor might suggest progesterone supplements if there are factors that could affect egg implantation or early pregnancy. You might be prescribed progesterone if you:
Are over the age of 35
Have a history of miscarriage
Show signs of a luteal phase issue
Have a thinner uterine lining
Are using ovulation induction medications
Are facing an unexplained infertility condition
Have a history of low progesterone level
Are managing conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or endometriosis
For more information about whether progesterone supplementation after an IUI treatment is necessary for your fertility condition, schedule an appointment with Thomson Fertility Centre.
Is there any reason why I should not take progesterone after IUI?
Although progesterone supplements are generally safe and can support early conception, it doesn't mean your fertility specialist will necessarily recommend this treatment, particularly if you have:
Liver disorders
A history of progesterone sensitivity
Heart or cardiovascular conditions
History of blood clots
Previous breast or reproductive cancers
Kidney problems, seizures, or severe migraines
Depression or mood disorders
Unusual vaginal bleeding not related to fertility treatment
Adequate natural progesterone levels
Your fertility specialist will review your complete medical history and current hormone levels before recommending progesterone supplementation. Your fertility specialist will carefully assess your individual fertility conditions to tailor this hormonal treatment plan to your needs.
Our fertility specialists
Loading...
How is progesterone administered?
Once you have undergone intrauterine insemination and are considered suitable for this hormonal treatment, your fertility specialist will select the most suitable progesterone administration method for you. Progesterone is usually administered in one of three ways:
Vaginal suppositories or gel:
The most common method of administration is via vaginal suppositories or gel, which are directly inserted into the vagina.
This method is preferred because it delivers the highest progesterone levels directly in your uterine lining, with fewer side effects throughout your body.
Oral tablets:
Another method is oral tablets, which are convenient and easily consumed. However, they may cause more general side effects and don't achieve quite as high progesterone levels in your uterus as vaginal methods.
For this reason, they are often used alongside vaginal suppositories to provide additional hormonal support.
Intramuscular (IM) injection:
The final method of administration is intramuscular injection into your buttock muscle.
This method is most commonly used in in vitro fertilisation (IVF) procedures and can deliver higher progesterone levels into the bloodstream.
What are the risks of taking progesterone supplements?
Just like any other hormonal medication, taking progesterone supplements may result in side effects. However, there is no need to worry, as the effects are usually mild and temporary, depending on how the hormone is delivered (orally, vaginally, or by injection).
Common side effects that might occur include:
Breast tenderness or swelling:
As progesterone prepares your body for potential pregnancy, it naturally triggers changes in breast tissue.
Similar to early pregnancy symptoms, this tenderness is completely normal and indicates that your body is responding to the hormone.
Bloating and digestive discomfort:
Taking progesterone, especially orally, has a relaxing effect on the muscles in your digestive tract. Such effects can slow digestion and cause mild bloating, constipation, or nausea.
Fatigue and mood changes:
Progesterone can affect the brain by binding to receptors that influence mood and alertness. As a result, you may feel more worn out than usual, experience mood swings, feel emotionally sensitive, or experience drowsiness.
Mild cramping and headaches:
As hormone levels fluctuate after progesterone injections, you may experience headaches or mild pelvic cramping. These symptoms may resemble those experienced during early pregnancy or premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
Vaginal discharge or leakage:
If you are given vaginal progesterone treatment, such as suppositories or gels, it can lead to discharge or leakage. Such discharge is usually not a cause for concern unless it is accompanied by irritation or infection.
Discomfort at the injection site:
If progesterone is administered by intramuscular injection, it is usually given in the gluteal muscle using a long needle, which can be uncomfortable.
Common side effects at the injection site include redness, swelling, bruising, and muscle soreness.
Keep in mind that having these side effects doesn't always mean something is wrong, they could just mean that the progesterone is doing its job. One common concern is whether progesterone delays your period after IUI, which is a normal effect of the supplementation. But if you have any severe or long-lasting symptoms, you should consult your fertility doctor.
If you're experiencing prolonged side effects or have concerns about your progesterone supplementation, schedule an appointment with Thomson Fertility Centre. Our fertility specialists can help manage any unusual side effects and ensure you feel supported throughout your fertility journey.
FAQ
How effective is IUI with progesterone supplementation?
The success of IUI when combined with progesterone support depends on several factors, including your age, the underlying cause of infertility, and your specific treatment protocol.
If you are under 35, the pregnancy rate per IUI cycle with progesterone support is generally around 15 to 25%.
When should I take progesterone after IUI?
It is usually recommended that you begin taking progesterone supplements about 24 to 48 hours after your intrauterine insemination procedure. This is usually continued until your next period starts or a pregnancy is confirmed.
If you do become pregnant, progesterone supplements are typically continued until around 8-12 weeks of pregnancy, by which time the placenta naturally takes over hormone production.
Does progesterone help implantation?
Yes, progesterone plays a vital role in helping embryos to implant in the womb. It does this by thickening and stabilising the uterine lining of the uterus, improving blood flow, and relaxing the uterine muscles to reduce contractions.
These effects make the womb more receptive, creating the ideal environment for a fertilised egg to implant and develop.
Why do they check progesterone levels after IUI?
Having your progesterone level checked around 5-7 days after ovulation (known as the mid-luteal phase) provides your doctor with valuable information. It confirms whether you have ovulated and whether your body is producing sufficient progesterone to support a potential pregnancy.
What are some ways to increase the chances of conception after IUI?
Here are some tips to help improve your chances of conceiving following an IUI procedure:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in protein, antioxidants, omega-3s, and vitamins
- Drink 2–3 litres of water daily to stay hydrated
- Maintain a healthy BMI to support fertility
- Do moderate exercise like walking or swimming
- Get 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night
- Avoid smoking and alcohol, as they can lower success rates
What should you avoid before an IUI procedure?
To support a successful IUI, here are key things to avoid:
- No ejaculation for 2–5 days before IUI
- Avoid high stress
- Skip strenuous exercise
- Avoid smoking and alcohol
- Stay away from hot baths, saunas, and hot tubs
- Limit caffeine intake
The information provided is for general guidance only and should not be considered as medical advice. For a personalised fertility consultation and tailored advice, schedule a consultation with Thomson Fertility Centre today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Fertility
- Paragon: 6252 7766
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Request an Appointment