Gonorrhoea is a common yet often overlooked sexually transmitted infection that can affect anyone who is sexually active. Many people do not realise they have it, as the symptoms can be mild or even go unnoticed.
If left untreated, it can cause serious health problems, including infertility. To help you take care of your sexual health, let's look at what causes gonorrhoea, what signs to look out for, and how you can protect yourself.
What is gonorrhoea?
Gonorrhoea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by a bacterium called Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It mainly affects the genital tract but can also infect the rectum, throat, eyes, and joints. One of the main concerns about gonorrhoea is that many people have no symptoms, so the infection can go undetected and spread more easily.
If left untreated, gonorrhoea can cause serious complications. These include pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), infertility, and, in rare cases, life-threatening conditions.
How gonorrhoea spreads
The bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae is spread through unprotected sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral, with an infected person. The bacteria grow in warm, wet areas of the body, such as the cervix (lower part of the womb), uterus (womb), urethra, rectum, and throat.
Sometimes, the bacteria can get into your eyes if infected genital fluids come into contact with them, such as through touching your eyes with contaminated hands. During childbirth, a mother who is infected can pass the bacteria to her baby, which can cause eye infections in newborns (known as ophthalmia neonatorum).
You cannot catch gonorrhoea just by hugging someone, sharing food or using the same toilet seat. The best way to stay protected is to practise safe sex and get tested regularly, especially if you have new or multiple partners.
Who is at risk of gonorrhoea?
While anyone who is sexually active can get gonorrhoea, certain factors can increase the risk of infection. Which include:
Younger adults, especially those under 25, as this age group tends to have more than 1 sexual partner.
Have sexual intercourse with more than one person or a new partner who hasn't been tested for STIs.
Have had a sexually transmitted infection (STI) in the past, which increases your risk of infection.
One of the main reasons people get gonorrhoea is because they don't always use condoms, known as condomless sex. The best ways to lower your risk and protect yourself and your partner are to use protection and get regular sexual health screenings.
Want to stay proactive about your sexual health? Request an appointment with us for STI screenings or consultation to ensure peace of mind and early detection.
Common symptoms of gonorrhoea
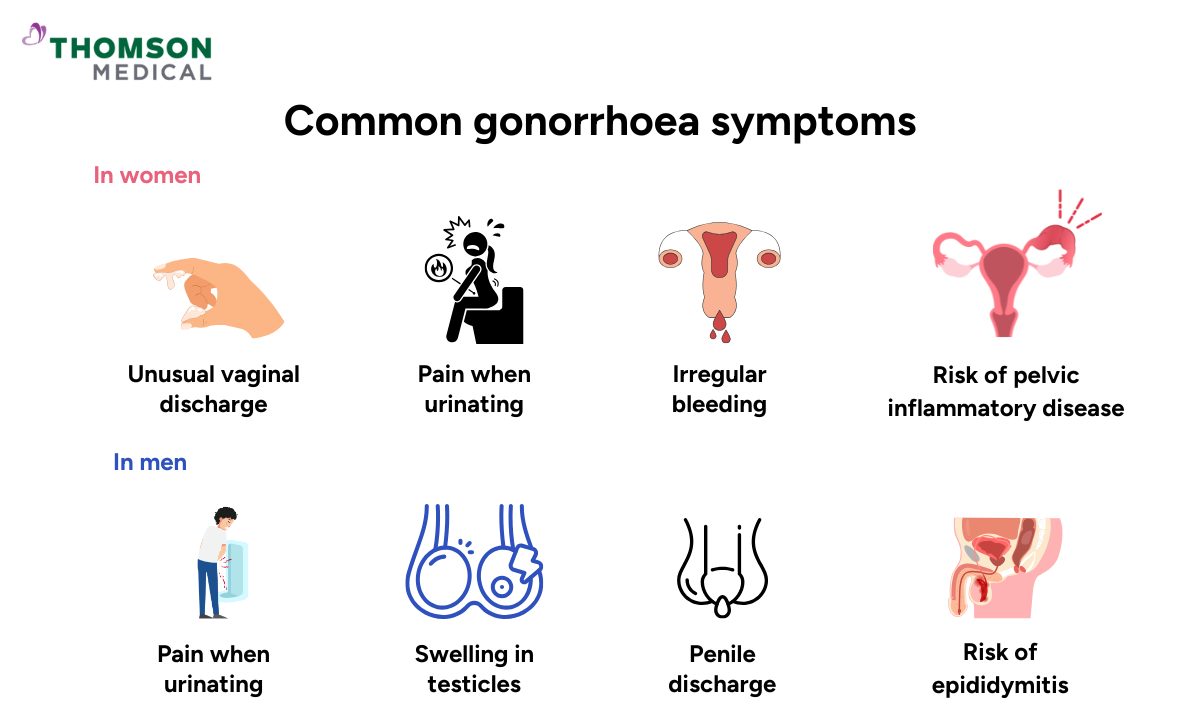
Gonorrhoea symptoms in women
In women, gonorrhoea usually affects the cervix, but it can also spread to other parts of the reproductive tract. The most common symptoms are:
Unusual vaginal discharge that may be thicker, yellowish, or slightly green
Pain or a burning sensation when urinating
Irregular vaginal bleeding, such as between periods or after intercourse
These signs can look like a urinary tract infection (UTI) or a yeast infection, so gonorrhoea can go unnoticed for some time. If not treated quickly, the infection can spread to the uterus and fallopian tubes, causing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). This is a serious condition that can lead to long-term pelvic pain, infertility, or an ectopic pregnancy.
Gonorrhoea symptoms in men
In men, gonorrhoea usually affects the urethra, the tube that carries urine and semen through the penis. The most common symptoms include:
Pain or burning when urinating
A frequent or urgent need to pass urine
Penile discharge that may be white, yellow, or green in colour
Swelling or pain in the testicles (less common)
Men are more likely to spot gonorrhoea early because symptoms often appear sooner. And, if you don't get treatment, the infection can spread to the epididymis, which is a tube behind the testicles that stores and carries sperm. This can cause painful swelling called epididymitis, which, if severe or long-lasting, can affect fertility.
It is very important to diagnose the infection early and to start antibiotic treatment as soon as possible to clear the infection and prevent long-term complications.
Gonorrhoea symptoms in both sexes
In both men and women, gonorrhoea can affect areas beyond the reproductive tract, leading to a range of symptoms depending on where the infection occurs.
Rectal gonorrhoea may cause pain, itching, discharge, or bleeding around the anus.
Oral gonorrhoea, contracted through oral intercourse with an infected partner, can result in a sore throat or swollen glands, though it may sometimes go unnoticed.
Eye infections (such as neonatal conjunctivitis) are rare but serious, causing redness, swelling, pain, and pus-like discharge. Immediate treatment is needed to prevent lasting damage to vision.
If you notice any symptoms of gonorrhoea or have concerns about your sexual health, request an appointment with Thomson Medical today for further testing and personalised care.
Our sexual health specialists
Loading...
How is gonorrhoea diagnosed?
Because gonorrhoea symptoms can be mild or mistaken for other infections, a laboratory test is the only reliable way to confirm the diagnosis. Your doctor will begin by taking a detailed sexual and medical history, followed by simple tests to detect the bacteria.
For men, a urine sample is commonly used to check for the presence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
For women, a swab from the cervix or vagina provides the most accurate result.
Rectal or throat swabs may also be taken if there has been anal or oral sexual contact.
The most widely used method today is the nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT), which detects the bacteria’s genetic material with high sensitivity and accuracy. In some cases, doctors may also perform a culture test, particularly when antibiotic resistance is suspected. This helps identify the most effective medication for treatment. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial to prevent complications and stop the infection from spreading.
How is gonorrhoea treated?
Gonorrhoea is treated with antibiotics, usually a single injection and some pills. Antibiotics don't always work, so doctors often use a combination of different medicines to make sure the infection is completely cleared.
It's important to finish the full course of treatment, even if symptoms get better, to stop the infection from coming back or becoming resistant to treatment. If you have intercourse with someone, you should be treated together, as you can easily get infected again. You should avoid having intercourse until your treatment is complete and follow-up tests confirm that you are better.
In Singapore, gonorrhoea treatment is available at general practitioners (GP), polyclinics, and sexual health clinics.
Complications of gonorrhoea
If gonorrhoea is not treated quickly, it can cause serious health problems for both men and women.
In women, the infection can spread to the uterus and fallopian tubes, causing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). This can cause ongoing pelvic pain, infertility, or an ectopic pregnancy, where a fertilised egg grows outside the womb.
In men, untreated gonorrhoea can affect the epididymis – the tube that carries sperm – leading to epididymitis, a painful condition that can reduce fertility.
Both men and women can sometimes get bacteria into their blood, which can cause a serious infection called disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI). Though rare, this can result in joint pain, skin rashes, heart valve infections, or meningitis, which require urgent medical care.
Gonorrhoea can also increase the risk of HIV transmission, as swollen, red skin around the genitals makes it easier for the virus to spread.
It is very important to get tested and treated early to stop these diseases from worsening or spreading and protect your fertility.
Prevention of gonorrhoea

You can lower your risk of gonorrhoea by following these key prevention steps:
Practise safe sex:
Use condoms correctly and consistently during vaginal, anal, and oral intercourse.
Have a monogamous relationship:
Stay with one partner who has tested negative for sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Get regular STI screenings:
It is generally recommended, especially if you have multiple or new sexual partners.
Do not rely on symptoms:
Gonorrhoea often has no obvious signs, so regular testing is important.
Communicate openly with partners:
Discuss STI testing and sexual health honestly between you and your partner.
Seek prompt medical care:
You should always visit a doctor if you notice any unusual discharge, pain, or discomfort.
Stay informed:
While there is no gonorrhoea vaccine yet, safe sexual practices and early detection remain the best protection.
To help protect your sexual health – request an appointment with Thomson Medical for confidential STI testing, personalised advice care.
FAQ
How long does it take for gonorrhoea symptoms to appear?
You usually start to show symptoms of gonorrhoea 2 to 14 days after being exposed to the disease. But some people may have mild or delayed symptoms, or no symptoms at all. This is more common in women, so it's important to get tested regularly after unprotected sexual intercourse or if you think you might have been exposed.
What does gonorrhoea look like?
The appearance of gonorrhoea depends on where the infection occurs:
Men, thick yellow or green penile discharge, redness at the urethral opening.
Women, watery or yellowish vaginal discharge, sometimes with light bleeding between periods.
Rectal infection, anal pain, discharge, or itching.
Oral infection, persistent sore throat.
Severe cases, skin rashes or joint swelling if the infection spreads through the bloodstream.
Can gonorrhoea go away on its own?
No, gonorrhoea cannot be cured without antibiotics. Even if the symptoms go away, the bacteria are still there and can cause problems like infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, or blood infections. The only way to clear the infection completely is with the right medical treatment.
How is gonorrhoea treated in men?
Men are treated with a combination of antibiotics, usually in the form of an injection and some tablets. This two-pronged approach gets around antibiotic resistance and makes sure the infection is fully cleared. Partners should be treated at the same time, and sexual activity should be avoided until follow-up tests confirm that they have recovered.
How long does gonorrhoea last in men?
If you get treated quickly, gonorrhoea usually clears up within a week. If it's not treated, it can last for months and cause pain in the testicles, swollen testicles (epididymitis) and even infertility. It's important to test for and treat any problems early to make sure you can still have children in the future.
What should you avoid if you have gonorrhoea?
You should:
Avoid intercourse until your doctor confirms the infection has cleared.
Ensure all partners are treated to prevent reinfection.
Limit alcohol while taking antibiotics to avoid side effects.
Do not self-medicate or use leftover antibiotics, as this may lead to drug resistance.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice based on your unique situations, please consult a specialist at Thomson Medical. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Novena:
6592 6686 (Call), 8611 8986 (WA) - Bukit Batok:
6569 0668 (Call), 8686 3525 (WA) - Choa Chu Kang:
6893 1227 (Call), 8282 1796 (WA) Jurong:
6262 8588 (Call), 6262 8588 (WA)- Katong (female doctor):
6970 2272 (Call), 8611 9020 (WA) - Punggol:
6243 6843 (Call), 8811 0328 (WA) - Sembawang: 6753 5228
- Sengkang: 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): 6382 3313
- Tampines: 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: 6276 1525
