It's understandable if you feel uncomfortable talking about sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). But, rest assured, getting the right information can help you to protect your health and make informed decisions about your care. The good news is that having the right information can help protect yourself and help catch infections before they cause serious harm.
What are STDs?
STDs are infections that spread primarily through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. You may also hear them referred to as STIs (sexually transmitted infections), since an infection can be present even when symptoms don't show up.
While the terms STI and STD are often used interchangeably, some use STI to refer to the infection itself, and STD when symptoms develop. However, many infections remain silent for weeks, months, or even years, which is why regular testing matters.
What causes STDs?
STDs develop from different types of organisms that can enter your body through intimate contact. Understanding what causes these infections can help you recognize how they spread.
These infections are caused by:
Bacteria such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis
Viruses including HIV, herpes, HPV, and hepatitis B
Parasites like trichomoniasis, which is caused by an organism that thrives in warm and moist environments.
Once these microbes enter your body, they can spread through various ways. Transmission happens through:
Sexual contact
Spread through sharing needles
Mother-to-baby transmission during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding
Infected blood through sharing needles or transfusions
Skin-to-skin contact in the genital area
How do STD symptoms show up in women?
One of the challenging aspects of STDs in women is that many infections produce no symptoms. You could be unaware that you are carrying an STD that could cause a health issues down the line.
When symptoms do appear, watch for these warning signs:
Abnormal vaginal discharge that differs from your normal pattern (different color, consistency, or smell)
Burning sensation or pain when you urinate, which many women initially mistake for a urinary tract infection (UTI)
Pelvic pain or discomfort in your lower abdomen
Pain during sex
Irregular vaginal bleeding that occurs between periods or after intercourse
Genital sores, bumps, or warts around your vulva (vaginal opening)
Swelling, redness, or itching in the vaginal area
As these symptoms may be mistaken for other diseases, proper testing is the only way to determine the cause of your symptoms. For further information about STD testing, schedule an appointment with Thomson Medical. Our specialists can help provide thorough testing and personalised treatment plans in a non-judgmental environment.
Common STDs that affect women
Since each STI comes with its own risks and challenges, knowing the most common ones can help you spot if something feels off.
Here’s a quick guide to some of the most common symptoms in women you should be aware of:
| STD | Cause | Common symptoms in female | What you should know |
|---|---|---|---|
Chlamydia | Bacteria | Vaginal discharge, painful urination, and pelvic pain | Can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and infertility if untreated. Usually cured with antibiotics. |
Gonorrhoea | Bacteria | Discharge, burning during urination, and bleeding between periods | Can cause PID and infertility. Some strains resist certain antibiotics. |
Bacteria | Primary: painless sore Secondary: rash or fever Tertiary: organ damage | The condition progresses through various stages. Curable with antibiotics at any stage. | |
Virus (HSV-1 or HSV-2) | Painful blisters or sores and flu-like symptoms during first outbreak | Although there is no definitive cure, antiviral medications can help to manage symptoms and reduce outbreaks. | |
Genital Warts (HPV) | Human Papillomavirus | Small flesh-coloured bumps or clusters | Some strains cause cervical cancer. The HPV vaccine prevents high-risk strains. |
Hepatitis B | Virus | Fatigue, nausea, jaundice, and abdominal pain | This disease can become chronic and damage the liver. Vaccine available for prevention. |
HIV/AIDS | Human Immunodeficiency Virus | Early: fever, sore throat, fatigue Later: weakened immune system | There is no definitive cure, but antiretroviral therapy (ART) is recommended for everyone with HIV. |
Trichomoniasis | Parasite | Yellow-green discharge with odour, itching, painful urination | Often no symptoms. Easily cured with antibiotics. |
When should you get an STD test?
Knowing when to seek testing can make the difference between catching an infection early and potentially experiencing complications later on.
Consider getting tested if you're in any of these situations:
You're sexually active especially with new or multiple partners
Symptoms appeared such as unusual discharge, sores, burning, or any discomfort
Starting a new relationship
Unprotected sex
You're pregnant or planning pregnancy
Needle sharing or blood exposure
Unlicensed piercing and tattoos
Why is STD testing so important?
You might wonder why testing is necessary if you have no symptoms. The truth is testing plays a role in your long-term health:
Prevents serious complications such as infertility, cancer, or organ damage
Peace of mind knowing your and your partner’s status
An early diagnosis can help to treat most bacterial STDs with antibiotics and manage viral infections to prevent complications.
Although STD testing might feel awkward or unnecessary when you feel healthy, but a doctor can guide you through the process, and recommend treatment or next steps to keep you safe.
Our specialists
Loading...
How are STDs treated?
Treatment varies depending on what type of infection you have, but most STDs respond well to medical intervention when caught early.
Antibiotics
Treat bacterial and parasitic infections. If you have chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, or trichomoniasis, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics. Always finish the full course, even if you feel better. Avoid an intercourse for at least a week after treatment and until any sores have healed.
Antiviral medications
Control viral infections like herpes and HIV. For herpes, they ease symptoms, shorten outbreaks, and lower the risk of passing it on. For HIV, ART keeps the virus in check, supports your immune system, and reduces transmission risk when taken properly.
How can you prevent STDs?
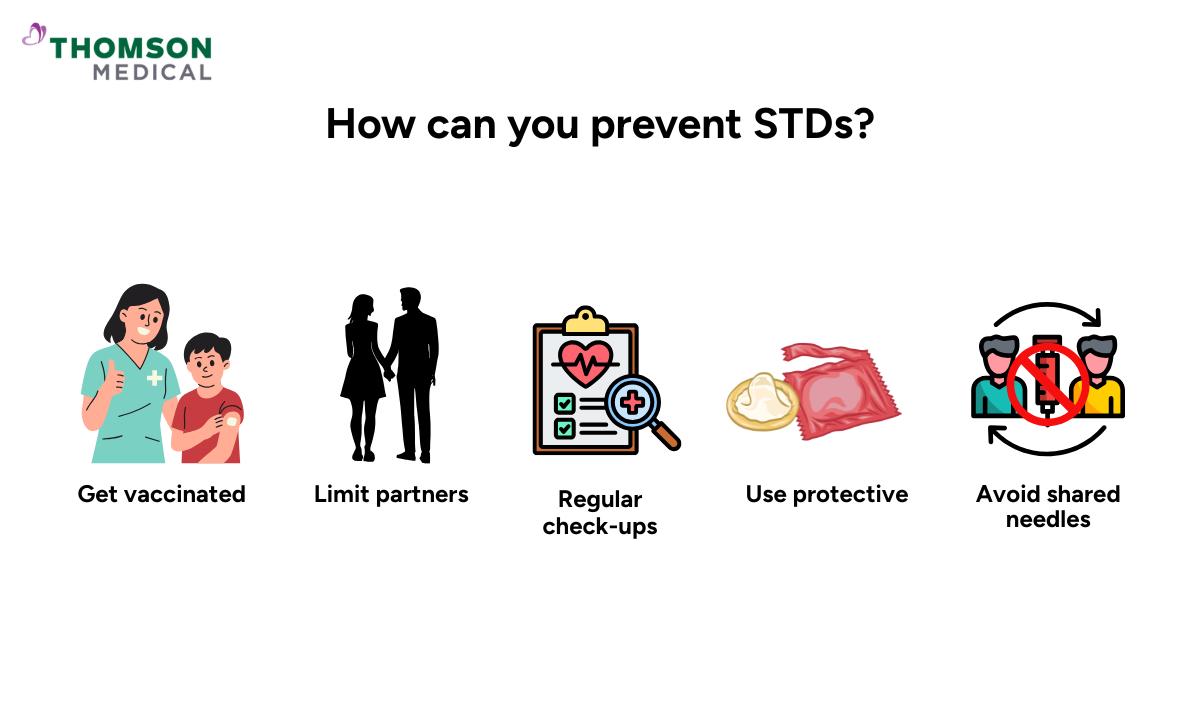
Prevention strategies work best when combined, creating multiple layers of protection against infection.
Getting vaccinated for hepatitis B and HPV
Limiting sexual partners
Practicing safe sex such as the partners using condoms or dental dams
Avoiding shared needles
Scheduling regular check-ups with your healthcare provider
keeps you informed about your sexual health status. These visits offer opportunities to discuss any concerns, review symptoms, and decide on appropriate testing intervals based on your individual risk factors.
Where can you get tested and vaccinated?
There are many easy ways to get STD testing and vaccinations in Singapore. Public polyclinics and hospitals offer subsidised testing, while private clinics provide faster, confidential services.
Specialized sexual health clinics offer anonymous testing options for those who prefer additional privacy. At-home test kits are also available for certain infections, allowing you to collect samples privately.
If you are concerned about your sexual health or have experienced any symptoms, schedule an appointment with Thomson Women’s Clinic. Depending on your needs, our specialist can recommend relevant tests. All consultations are conducted in a confidential and professional setting, with sensitivity to your concerns.
FAQ
What are the first signs that you have an STD?
Early warning signs often include unusual discharge, pain or burning while urinating, genital sores or warts, itching or redness in the genital area, and pain during sex. However, many STDs have no symptoms at all initially, which is why testing matters even when you feel fine.
What causes STDs in females?
Women develop STDs from the same microbes as men which are bacteria, viruses, and parasites. However, women face higher susceptibility due to anatomical differences (more exposed mucous membranes in the vaginal area), hormonal fluctuations that affect the vaginal environment, and the organisms often stay asymptomatic in women.
What happens when a woman has an STD?
Many women initially show no symptoms. Without treatment, STIs can lead to PID, infertility, chronic pelvic pain, complications during pregnancy, and an increased risk of transmitting HIV. Some viral STDs, such as HPV, can cause cervical cancer, while others, such as HIV and herpes, cause lifelong infections that require ongoing treatment.
How can you check yourself for an STD?
Start by monitoring your body for any of the symptoms. At-home testing kits are available for certain STDs, such as chlamydia, gonorrhoea and HIV. However, the most reliable approach is to visit a healthcare provider for a comprehensive STD screening.
Which STD makes you urinate frequently?
Both chlamydia and gonorrhoea can cause frequent urination, as well as a burning sensation. These symptoms closely mimic those of a UTI, which is why many women initially misidentify what they are experiencing. If you experience these symptoms, it is important to get tested to determine the actual cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Can virgins get STDs?
Yes, some infections, such as HPV and herpes, are transmitted through skin-to-skin contact in the genital area. Others can be passed on through oral sex or other intimate contact. Some infections can be transmitted through non-sexual routes, such as blood transfusions or sharing needles, or from mother to baby during childbirth.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice based on your unique situations, please consult a specialist at Thomson Medical. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Novena:
6592 6686 (Call), 8611 8986 (WA) - Bukit Batok:
6569 0668 (Call), 8686 3525 (WA) - Choa Chu Kang:
6893 1227 (Call), 8282 1796 (WA) Jurong:
6262 8588 (Call), 6262 8588 (WA)- Katong (female doctor):
6970 2272 (Call), 8611 9020 (WA) - Punggol:
6243 6843 (Call), 8811 0328 (WA) - Sembawang: 6753 5228
- Sengkang: 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): 6382 3313
- Tampines: 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: 6276 1525
