If you've been recommended a CA125 test, you might be wondering what it is and why your doctor ordered it. CA125 (cancer antigen 125) is a protein found in the blood, and higher levels can sometimes be linked to ovarian cancer – but they can also rise due to non-cancerous conditions, such as fibroids or endometriosis. While it isn’t used to screen for ovarian cancer in all women, this test helps doctors evaluate symptoms, monitor diagnosed ovarian cancer, or track treatment response.
This article explains the test and what your results mean so you can feel more informed about your care.
What is ovarian cancer?
When abnormal cells in your ovaries begin to grow and reproduce uncontrollably, it can lead to ovarian cancer. These cancerous cells can develop into tumours that harm neighbouring healthy tissues. They also spread to different parts of the body, including the liver, lungs, lymph nodes, and the lining of the abdomen.
The cancer can be caused by many factors, most commonly genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 or BRCA2, as well as certain lifestyle and environmental factors.
What makes ovarian cancer concerning is that its early symptoms are often vague and only become noticeable when the disease progresses.
The signs of this disease usually include:
Abdominal bloating or swelling
Weight loss
Changes in bowel habits
Frequent urination
Abnormal vaginal bleeding
Can CA 125 detect ovarian cancer?
CA 125 is a tumour marker – a substance that can indicate signs of disease. It is a type of protein often found on the surface of ovarian cancer cells and in some normal tissues.
The CA 125 test can help detect ovarian cancer. When you have ovarian cancer, CA 125 levels in your blood are elevated. However, high CA 125 levels don’t always mean you have cancer. There are some other conditions that can also raise the CA 125 levels, such as:
Menstruation
Pregnancy
Endometriosis
Liver disease
Because of this, the CA 125 test alone isn’t reliable for early detection. Your doctors may combine it with imaging tests or other biomarkers to confirm a diagnosis.
When to get CA 125?
Your doctor may recommend the CA 125 test to help you:
Screen if you’re at high risk:
If you have a family history of ovarian cancer or related cancer, or you carry BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations, your doctor may request regular CA 125 testing to monitor your health.
Evaluate a mass or abnormal growth:
If your doctor finds an ovarian mass, they may suggest a CA 125 test along with other tests to determine if it could be malignant.
Monitor ovarian cancer treatment:
This is the most common use. During treatment, regular CA 125 tests help your doctor know if the treatment is working for you. The frequency will depend on your treatment plan.
Check the recurrence after treatment:
After finishing the treatment, you may need periodic CA 125 tests to detect early signs if the cancer returns.
Your specific schedule will depend on your type of cancer, stage, and risk factors.
How is the CA 125 ovarian cancer marker test done?
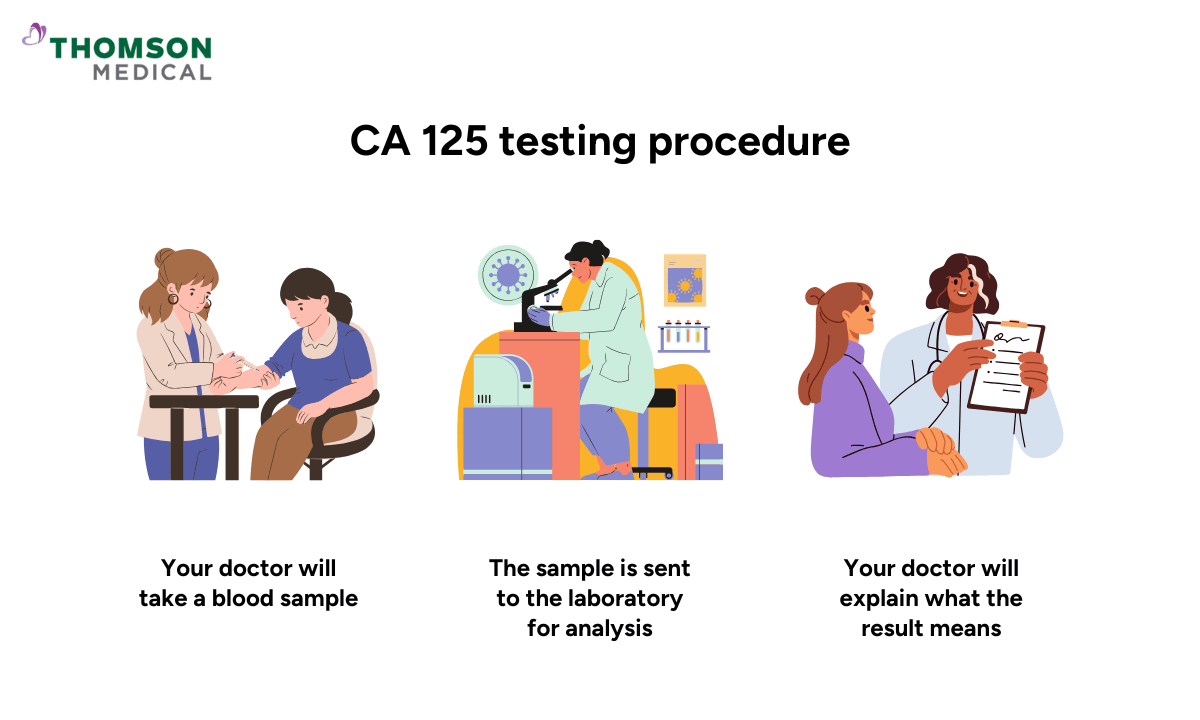
The CA 125 test is quick and straightforward. Your doctor will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm. You may feel a slight pinch when the needle goes in or comes out.
The sample is then sent to the laboratory to measure the level of CA 125 tumour markers in your bloodstream. You will usually receive the test result within a few days. Your doctor will help you explain what the result means for you.
If you’re unsure about what the CA 125 is for or how it works, schedule an appointment with our obstetricians and gynaecologists at Thomson Medical to discuss your concerns and get expert, personalised guidance.
Our women's cancer specialists
Loading...
What your CA 125 test results mean?
Your doctor will interpret your CA 125 test result as follows:
0–35 units/mL:
This is considered normal and usually means there is no sign of cancer.
Above >35 units/mL:
The level is higher than normal, which may suggest possible ovarian cancer. In this case, your doctor may recommend additional tests to find out.
Not all patients with elevated CA 125 levels have cancer. If you don’t have a history of ovarian cancer, your doctor may recommend additional tests to find out the cause.
If you’ve had ovarian cancer before, a rising CA 125 level could suggest that the cancer has returned, so your doctor may monitor it regularly.
Why one test isn't enough?
CA 125 levels can fluctuate for different reasons – such as menstruation, pregnancy, or benign conditions like endometriosis.That’s why a single test can’t tell the whole story. For an accurate diagnosis, your doctor will review your CA 125 results together with your symptoms and other test results.
What happens if your CA 125 level is high?
If your CA 125 test comes back elevated, don’t panic. It doesn’t always mean you have cancer. Your doctor will take a systematic approach to find out what's causing the elevated level.
You may be suggested to take:
Physical examination:
A thorough pelvic exam can detect any abnormal changes in your reproductive organs.
Imaging tests:
Depending on your exam results and symptoms, you may need a transvaginal ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI scan to get detailed images of your pelvic area.
Additional blood tests:
These can help rule out non-cancerous conditions that might be raising your CA 125 level.
Depending on your situation, your doctor may recommend one of the following approaches:
If the imaging and exam don’t show anything concerning:
Your doctor may recommend monitoring your CA 125 level over time.
If the imaging and exam show a suspicious mass:
You may need a biopsy or surgery to examine the tissue.
Throughout this process, be sure to share all relevant information with your doctor – including your menstrual cycle timing, pregnancy status, or any conditions like endometriosis – as this helps them interpret your results accurately.
How to manage CA 125 levels?
If your CA 125 levels are elevated, there are medical treatments and lifestyle changes that may help influence the level.
Medical treatment:
For ovarian cancer, treatment may include surgery to remove the tumour, followed by chemotherapy. These treatments directly target cancer cells and result in decreasing CA125 levels.
Healthy lifestyle:
The CA 125 level is affected by many factors, and lifestyle changes alone can not lower its levels caused by cancer. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can support your body during treatments and improve treatment outcomes. The approaches include:
Eating a balanced diet
Exercising regularly
Managing stress
Getting enough quality sleep
Minimising exposure to environmental toxins.
Taking care of your physical and emotional health can help your body cope with treatment and enhance your long-term well-being.
Waiting for or worrying about your CA 125 test can be stressful, but you don’t have to face it alone. Our specialists at Thomson Medical will walk you through every step. Schedule an appointment today for clarity, reassurance, and personalised care.
FAQ
Will I need to do anything to prepare for the test?
No, the CA 125 blood test is quick and usually doesn’t require any special preparation.
Some women prefer to schedule the test when they're not menstruating, because periods can elevate CA 125 levels slightly. You can inform your doctor about your current stage in your cycle in advance.
How common are false results?
False results can happen. That’s why CA 125 isn't used alone for diagnosis.
The result can be:
False positives:
The test shows a high CA 125 level but no cancer. This is common because many benign conditions can raise CA 125. That's why doctors always use CA 125 alongside other tests.
False negatives:
The test shows a normal CA 125 level, but cancer is present. Not all ovarian cancers produce elevated CA 125, especially in early stages or certain cancer types.
For a more accurate diagnosis, your doctor may suggest other tests along with CA125.
Are there risks to a CA 125 blood test?
No. The CA 125 test is very safe. As with any blood draw, you might experience slight pain or a pinch when the needle goes in. In a very rare case, you might feel lightheaded or faint.
However, these effects are minimal and temporary. Your doctor will gently guide you through the process to make sure you feel comfortable.
Should I be having regular CA 125 blood tests?
This depends on your situation. Your doctor may recommend regular CA 125 tests if you are at high risk due to genetic mutations or a family history of ovarian cancer, or if you have been diagnosed with the cancer.
You may not need regular CA 125 tests if you have no symptoms and are at average risk. To be sure, your doctor will work with you and help you determine what’s right for you.
Is CA 125 a good screening test for ovarian cancer?
CA 125 is not recommended as a routine screening test for ovarian cancer in women at average risk.
Its effectiveness depends on the stages of cancer. The study shows that it detects about 75–90% of advanced-stage ovarian cancers but only about 50% of early-stage cases. Because early detection is crucial for better outcomes, this low sensitivity in the early stages limits its usefulness as a screening tool.
However, CA 125 is more useful for monitoring treatment responses or checking for recurrences in women already diagnosed with ovarian cancer.
Which cancer marker is elevated in ovarian cancer?
CA 125 is the most famous tumour marker for ovarian cancer. However, there are some other markers that may be used alongside CA 125 for better accuracy, especially in complex cases. They include:
HE4 (Human Epididymis Protein 4)
AFP (Alpha-fetoprotein)
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations based on your medical conditions, request an appointment with Thomson Medical.
References:
Moss, E. L., Hollingworth, J., & Reynolds, T. M. (2005). The role of CA125 in clinical practice. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 58(3), 308–312. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.2004.018077
Matsas, A., Stefanoudakis, D., Troupis, T., Kontzoglou, K., Eleftheriades, M., Christopoulos, P., Panoskaltsis, T., Stamoula, E., & Iliopoulos, D. C. (2023). Tumor markers and their diagnostic significance in ovarian cancer. Life, 13(8), 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13081689
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Novena:
6592 6686 (Call), 8611 8986 (WA) - Bukit Batok:
6569 0668 (Call), 8686 3525 (WA) - Choa Chu Kang:
6893 1227 (Call), 8282 1796 (WA) Jurong:
6262 8588 (Call), 6262 8588 (WA)- Katong (female doctor):
6970 2272 (Call), 8611 9020 (WA) - Punggol:
6243 6843 (Call), 8811 0328 (WA) - Sembawang: 6753 5228
- Sengkang: 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): 6382 3313
- Tampines: 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: 6276 1525
Dr Wang Junjie
Obstetrics & Gynaecology (O&G)
Thomson Women's Clinic & Cancer Surgery
English, Mandarin
Prudential, Alliance MediNet

