If you've noticed small, flesh-coloured bumps in your genital area, you're probably feeling concerned, confused, and perhaps embarrassed. What are they? How did they appear? Most importantly, how can they be effectively treated?
These growths could be genital warts, which are a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by certain types of HPV. The good news is that multiple effective treatments are available in Singapore that can remove the warts and help you regain your confidence.
What are genital warts?
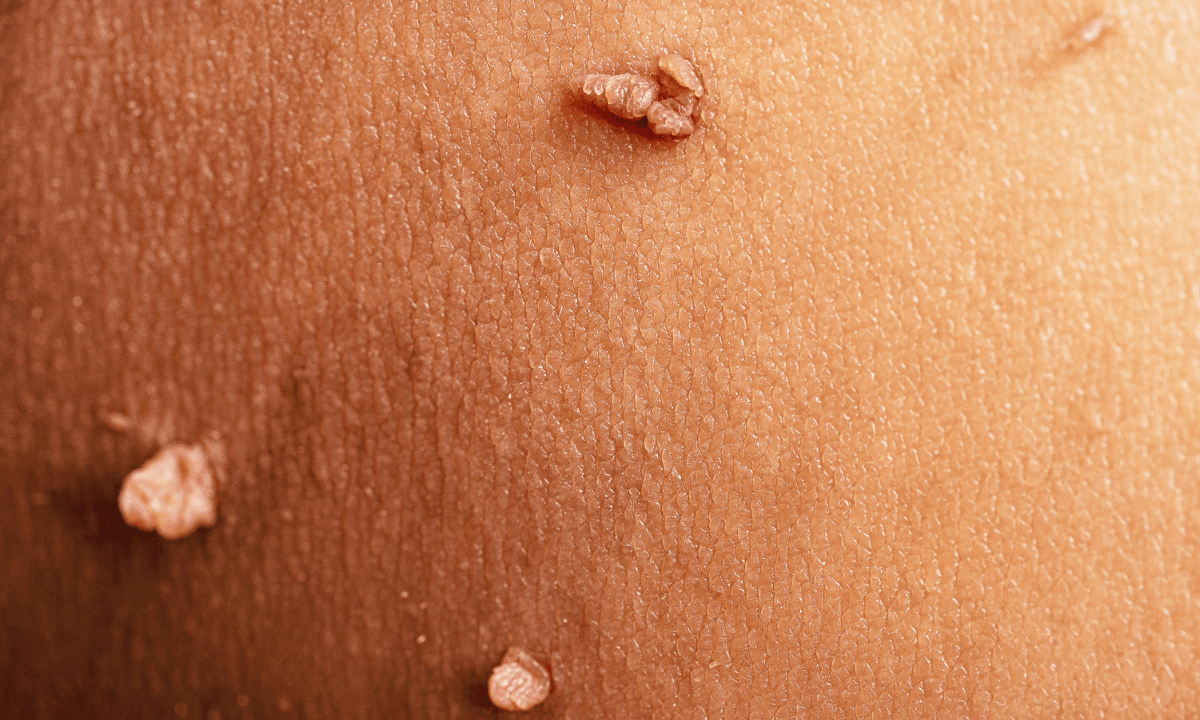
Genital warts are a common STI caused by low-risk types of human papillomavirus (HPV), such as HPV-6 and HPV-11. They appear as small, flesh-coloured bumps or growths in the genital and anal areas, and they may resemble cauliflower. Occasionally, they are so small that you can't see them with the naked eye.
Genital warts usually don't hurt, but they can make you feel uncomfortable and itchy. They can be spread through sexual activity, touching genitals (skin-to-skin contact without ejaculation), and oral intercourse. You can have the type of HPV that causes genital warts without developing any symptoms, which means you might unknowingly pass HPV to your partner.
In Singapore, you can seek treatment for genital warts at public or private hospitals, specialised STD clinics, or non-governmental organisations (NGOs). Both dermatologists and obstetrician and gynaecologist (O&G) specialists can diagnose and treat this condition.
How are genital warts diagnosed?
To treat these warts, your doctor will start by examining the affected area visually. The appearance of the warts is usually enough to confirm the diagnosis. However, if there is any uncertainty or the warts look unusual, your doctor may take a small tissue sample (biopsy) and send it to a lab for examination.
For women, your doctor may recommend additional tests during your appointment. These tests don't diagnose warts themselves, but they do search for changes in cervical cells and high-risk HPV strains, like HPV-16 and HPV-18, that can cause cervical cancer. This test is important because having one type of HPV doesn't mean you can't have other types. These tests include:
Pap test:
A Pap test, also known as a Pap smear, involves collecting a cell sample from the cervix (the lower part of the womb) and vagina to detect cellular abnormalities caused by HPV infection.
HPV test:
The HPV test is a screening tool used to detect high-risk strains of the human papillomavirus. It involves analysing sample cells taken from the lower end of the womb (cervix).
It's often performed alongside a routine Pap test, where a sample of cervical cells can be tested for these cancer-causing HPV strains.
Colposcopy:
A colposcopy examination allows your doctor to see your cervix, vagina and vulva more clearly than a regular Pap smear. It is usually performed after an abnormal screening test.
These tests can be performed as part of routine sexual healthcare for women, since HPV infections often cause no symptoms and detecting cervical cell changes early can help prevent cancer.
Since other conditions such as moles, skin tags, or other STIs can resemble genital warts, doctor diagnosis is essential to ensure you receive the right treatment. If you think you might have genital warts, schedule a confidential appointment with Thomson Medical. Our specialists provide compassionate, judgement-free care and will work with you to determine the best treatment for your condition.
Our specialists who can treat warts
Loading...
Genital wart treatments
Although genital warts may clear up within two years as your immune system fights the infection, treatment is often recommended, since untreated warts can grow larger, multiply or cause discomfort. Removing the warts also lessens the likelihood of the infection spreading, as an active outbreak is more susceptible to transmission.
It's important to know that, while treatment effectively removes visible warts, it doesn't eliminate the HPV itself, meaning the condition can recur. But this doesn't mean that treatment is unnecessary, as it can relieve discomfort, lower the risk of spreading HPV, and rule out more serious conditions.
Think of genital warts treatment as a way of managing the condition, controlling recurrence, and maintaining your quality of life. The available treatment options for genital warts include:
Topical treatments (applied on skin)
A topical treatment uses a cream or ointment that is applied directly to the warts to reduce their size and number. These treatments either destroy wart tissue or stimulate the immune system to fight HPV. It can take up to 16 weeks for these treatments to become fully effective.
Here are some of the topical treatments your doctor may prescribe:
| Medication | How it works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
Imiquimod | Boosts immune system to fight HPV | This cream can be self-applied and is effective on small external warts. | Can cause redness, irritation, or itching |
Podofilox | Destroys wart tissue | Works within days to weeks and easy to apply at home | Cannot be used during pregnancy and may irritate healthy skin |
Sinecatechins | Green-tea extract, which act as an immune booster | Natural-based, effective for external genital warts and can prevent recurrence | Expensive and require longer treatment course (up to 16 weeks) |
Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) | Burns wart tissue | Applied by doctor, can be used during pregnancy | Painful and may need repeated sessions |
Procedural or surgical treatments
Other than topical treatments, you may need surgery to remove larger warts or those that do not improve with medication. If you are pregnant, you may need surgery to remove warts that your baby could come into contact with during birth. Surgeries for genital warts include:
| Method | How it works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
Cryotherapy (freezing with liquid nitrogen) | Freezes & destroys wart tissue | Quick and effective for multiple small warts | May need repeat sessions and may cause blisters |
Electrocautery (burning with electric current) | Burns off wart | Immediately remove the warts | Requires local anaesthesia during the procedure and may cause scarring |
Laser surgery help to vaporise wart tissue | Good for large, widespread, or resistant warts | Expensive and may requires anaesthesia (local or general) | |
Surgical excision | Surgical removal cuts out the wart | Removes large or complex warts in one go | May cause scarring and requires recovery time |
To help determine which is the most suitable treatment for your condition, it's recommended that you contact a specialist. Schedule a consultation with Thomson Medical for a confidential and tailored treatment.
Cost of genital wart removal in Singapore
The cost of treatment for genital warts in Singapore depends on several factors, including the number of warts, the area to be treated, the chosen method of treatment, and whether you seek care at a public or private healthcare facility.
Public settings
At public healthcare facilities, the consultation fee can range from SGD 40 to SGD 90. The cost of treatment per session can range from SGD 80 to SGD 200. Multiple sessions are often required for complete clearance, usually ranging from one to three sessions, depending on the treatment method and severity.
Private settings
In private settings, costs are usually higher, but greater flexibility is offered in terms of appointment scheduling. Consultations range from SGD 80 to 150. Here are some costs you can expect for treatment types:
Cryotherapy can cost SGD 80 per lesion to SGD 300 for 5 or more lesions.
Topical treatment costs vary based on the prescribed regimen and duration (up to 16 weeks).
Electrocautery or laser treatment, SGD 200-600 per session
Surgical excision can cost SGD 800-1,500 for complex cases.
Additional costs may include topical or oral medications prescribed to supplement treatment or for post-operative care. HPV vaccination (such as Gardasil 9) may also be recommended if you have not been vaccinated.
Unfortunately, STD treatment, including treatment for genital warts, is not covered by Medisave or the Community Health Assist Scheme (CHAS) in Singapore. However, some private health insurance plans may provide coverage, depending on the policy. To further reduce costs, some healthcare facilities in Singapore may offer subsidised or affordable tests.
The prices listed above are intended to serve as a general guide to help you estimate expected costs. Actual prices may vary depending on the clinic, the complexity of the treatment, and the number of sessions required. Contact our medical concierge team for a detailed price breakdown and a personalised treatment plan.
FAQ
What is the fastest way to get rid of genital warts?
Procedural treatments such as cryotherapy, electrocautery, laser treatment, or surgical excision usually remove warts more quickly than topical creams. These procedures can clear visible warts in one to three sessions, while topical treatments can take up to 16 weeks.
However, the "fastest" method depends on the size, number, and location of your warts. Your doctor will recommend the most suitable treatment for you.
Do genital warts ever fully go away?
Visible warts may disappear on their own or with treatment. However, the virus that causes genital warts can remain dormant even after the warts have gone. This means that warts can recur depending on the treatment method used and the condition of your immune system.
How can I treat genital warts by myself?
Only topical medications that have been prescribed to you, such as imiquimod or podofilox, are safe to apply to genital warts yourself. Never use over-the-counter wart removers intended for use on the hands or feet on your genitals, as these products contain harsh chemicals that could harm the sensitive skin in this area.
How do you treat genital warts in children?
As genital warts are uncommon in children and can be sensitive, they require careful medical evaluation by a paediatrician or paediatric dermatologist, who can properly assess the cause and provide appropriate treatment for the child's age.
Is there a cream that can be used to treat genital warts?
Yes, several prescription topical creams are available for treating genital warts. These include imiquimod, podofilox, and sinecatechins. These creams work in different ways, with some stimulating your immune system to fight HPV and others destroying wart tissue directly.
Treatment typically lasts from several weeks to 16 weeks, depending on the medication and how your body responds to it.
What causes warts in the genital area?
Genital warts are caused by an infection with low-risk strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly types 6 and 11. The virus spreads primarily through:
- Sexual intercourse (vaginal, anal, or oral)
- Skin-to-skin genital contact, even without penetration or ejaculation
- Vertical transmission during childbirth (though rare, from mother to baby)
It's important to note that you can have HPV and be contagious even if you have no visible warts. The virus spreads through direct contact with infected skin or mucous membranes.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations based on your specific conditions or needs, schedule a consultation with our specialists at Thomson Medical.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Novena:
6592 6686 (Call), 8611 8986 (WA) - Bukit Batok:
6569 0668 (Call), 8686 3525 (WA) - Choa Chu Kang:
6893 1227 (Call), 8282 1796 (WA) Jurong:
6262 8588 (Call), 6262 8588 (WA)- Katong (female doctor):
6970 2272 (Call), 8611 9020 (WA) - Punggol:
6243 6843 (Call), 8811 0328 (WA) - Sembawang: 6753 5228
- Sengkang: 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): 6382 3313
- Tampines: 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: 6276 1525
