Even if your Pap smear came back normal, some questions may still linger: "Does this mean I'm safe? Should I watch for symptoms?"
Your concerns are actually valid, and it's natural to look for clarity and reassurance when it comes to your health. While Pap smears are highly effective, they do have limitations. Knowing what they can and cannot detect will help you take the right steps to protect your cervical health.
What is a Pap smear test?
A Pap smear is a simple screening test that helps detect abnormal or precancerous cells on your cervix – often long before they become serious.
The main goal of a Pap smear is early detection. By catching abnormal cells before they turn into cancer, your doctor can treat or remove them, preventing cervical cancer from developing.
Sometimes, your doctor will combine a Pap test with an HPV test, which detects the human papillomavirus (HPV) – the main cause of cervical cancer. This combination, called co-testing, can help your doctor get a clearer picture of your cervical health.
How is a Pap smear done?
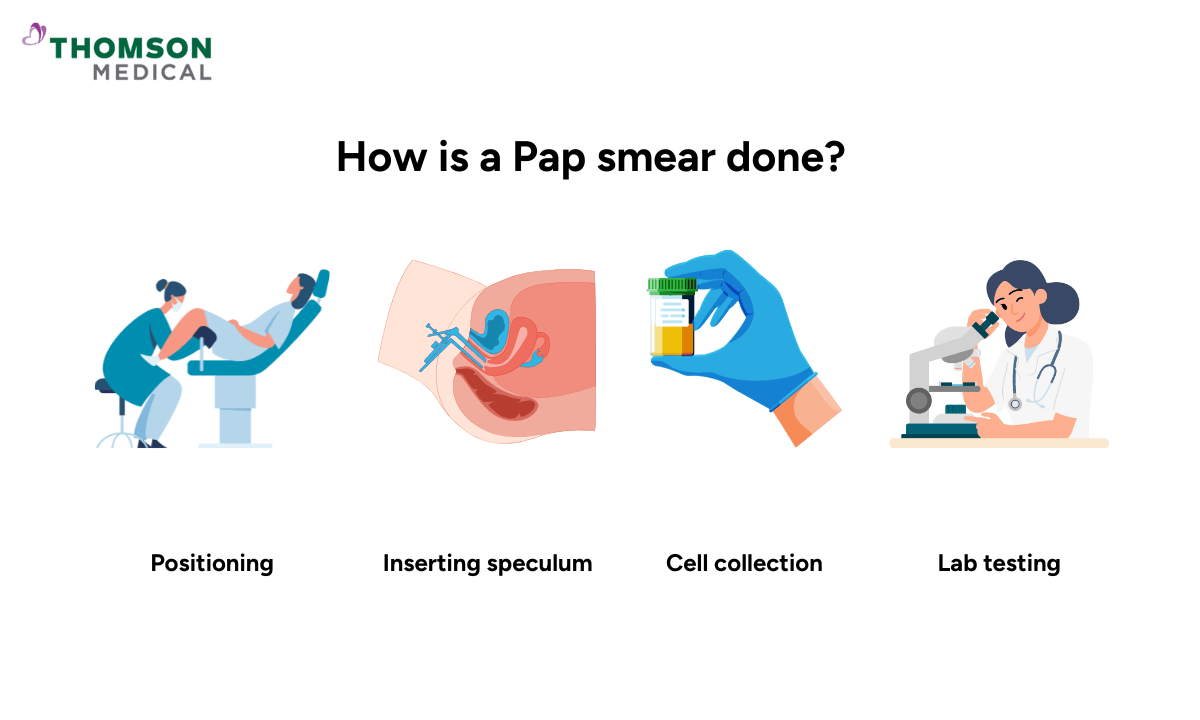
The Pap test is a simple and quick process, and your doctor will gently guide you through it step by step.
Here is what you can expect during the process:
Positioning:
You will lie on an examination table with your feet placed in stirrups.
Inserting speculum:
Your doctor will gently insert a speculum into your vagina to open it and see your cervix clearly.
Cell collection:
Your doctor uses a small brush or spatula to collect a sample of cells from your cervix.
Although it’s painless, you might feel a bit of pressure or discomfort. Don’t worry, it won’t last long.
Lab testing:
These cells are then sent to a lab to be examined under a microscope.
It’s normal to feel nervous before the test, so if you have any concerns, don’t be afraid to share them with your doctor. They can give you some advice to help you feel better during the process.
The test usually takes less than five minutes, and your results are available within a few days to a week. You can go back to your routine activities right after the test.
When and how often should you have a Pap smear test?
You can have your first Pap test at the age of 21. Your screening schedule will then depend on your age and health condition.
If you are between 21 and 29:
You should get a Pap smear every three years.
If you are between 30 and 65:
It’s recommended to have a Pap test every three years.
However, if you choose co-testing, you only need one every five years.
If you are over 65:
Your doctor may advise you to stop screening if you have had normal results for the past 10 years and no history of cervical abnormalities.
After hysterectomy:
If you have had a hysterectomy for non-cancer reasons, you may no longer need Pap testing.
However, if you have risk factors, such as a weakened immune system or previous abnormal results, your doctor may suggest more frequent testing. There is no need to worry; it’s just an extra step to look after your health. Your doctor will work closely with you and help set up a screening schedule that’s right for you.
What do Pap smear results mean?
The results of Pap tests are classified based on how cervical cells look under a microscope. Here is what your results may show:
Results | Meaning | Next steps |
Normal (negative) | No abnormal or cancerous cells were detected | Continue regular screening as scheduled |
ASC-US (Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Signature) | Minor, unclear changes that may be caused by infection or inflammation | Your doctor will suggest HPV testing or repeat Pap in 1 year |
LSIL (Low-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion) | Mild abnormal changes, often HPV-related | Further testing, such as an HPV test or colposcopy, is recommended |
HSIL (High-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion) | More severe changes that could develop into cancer if not treated | You may need a colposcopy and biopsy |
Atypical Glandular Cells (AGC) | Abnormal glandular cells that may indicate precancerous changes | Your doctor will recommend a colposcopy and further evaluation |
Cancer cells | This is a rare finding that indicates invasive cancer | You will be referred for treatment immediately |
While waiting for results can feel stressful, you won’t have to interpret them on your own. Your doctor will be there to help you understand what your result means for your situation and plan the next steps for you.
Not sure what your Pap test result means? Schedule an appointment with Thomson Medical. Our experienced healthcare professionals will help you understand the screening test results and recommend a personalised plan for your health.
Our women's cancer specialist
Loading...
What if you have an abnormal Pap smear?
It’s understandable to feel worried if your Pap test comes back abnormal. However, an abnormal Pap test doesn’t always mean you have cervical cancer.
Most of the time, it means mild cell changes, which are usually caused by HPV infection, inflammation, or hormonal changes.
Depending on your results, your doctor may recommend one or more of these follow-up tests to help them understand your cervix more clearly.
HPV testing:
It helps your doctor find high-risk HPV strains that can cause cancer.
Colposcopy:
It’s a detailed examination of your cervix using a magnifying instrument to identify abnormal areas.
Biopsy:
Your doctor will take a small tissue sample from your cervix and send it to the lab for analysis.
Repeat Pap test:
You will be recommended to have a repeat Pap test after a few months to monitor any changes.
While going through so many tests can feel a little overwhelming, each one provides crucial information that can help your doctor spot and identify any issues.
Early detection can be stressful, but it’s actually a positive thing. It allows your doctor to take action before cancer develops, and with the right follow-up care, you can successfully manage abnormal results.
Can you have cervical cancer with a normal Pap smear?
Even with a normal result, you might still wonder, “Can I still have cervical cancer?” It’s a common concern, and you’re not the only one who has this question.
It is possible to have cervical cancer with a normal Pap result, but this situation is rare. Several factors can explain this situation:
Sampling error:
It happens when not enough cells are collected or when abnormal cells are missed.
Hidden lesions:
Cancer may develop in areas that are difficult to reach during the sampling process.
Rapid progression:
In rare cases, precancerous changes progress quickly between screenings.
Non-HPV-related cancer:
Pap tests alone may not detect a small number of cervical cancers, like adenocarcinomas.
Even though these situations are rare, they highlight why it’s so important to pay attention to symptoms and keep up with regular screening. The two tests can support each other and catch what one test alone may miss.
If you experience vaginal bleeding (especially after sexual intercourse), pelvic pain, or unusual vaginal discharge, even if your last Pap test was normal, don’t hesitate to reach out to your doctor. It’s always better to check for your peace of mind.
If you're not sure which cervical cancer screening is right for you, schedule an appointment with Thomson Medical. Our healthcare professionals will guide you through your options and create a personalised care plan tailored to your needs.
FAQ
What is the difference between the Pap test and the HPV test?
Both the Pap test and the HPV test help detect cervical cancer, but they work in different ways:
Test | Purpose | What it detects |
Pap test | Screens for abnormal or precancerous cervical cells | Cellular changes on the cervix |
HPV test | Detects presence of high-risk HPV types | The virus that causes most cervical cancers |
If you don’t know which test is right for you, don’t worry. Your doctor will help you understand these tests and decide if they are suitable for your situation. In some cases, your doctor may combine both tests for more accurate screening and better protection.
What does it mean if your Pap is normal, but HPV is positive?
It means you have an HPV infection, but it hasn’t yet caused visible cell changes. This situation is actually more common than you might think. In this case, your doctor will likely suggest:
Repeat Pap and HPV testing in 12 months
Closer monitoring or colposcopy if high-risk HPV persists
Many HPV infections go away on their own, but persistent infections need careful follow-up. Your doctor will monitor you closely to make sure everything is under control.
How should I prepare for a Pap smear?
To ensure accurate results, there are a few things you should keep in mind:
Schedule your test when you are not on your period
Avoid intercourse until after the test
Try not to use vaginal creams, lubricants, or douches for 2–3 days before the test
Inform your doctor if you are pregnant, menopausal, or on medications
If you are unsure what to avoid and how to prepare for the test, check with your doctor beforehand.
Does a Pap smear hurt?
Most women describe it as mildly uncomfortable, but not painful. You may feel pressure or cramping when the speculum is inserted, but it goes away quickly.
However, if you feel anxious about the procedure, let your doctor know. They can take extra care to make sure you feel comfortable.
What are the disadvantages of a Pap smear?
A Pap test is usually safe and effective, but it still has limitations, including:
False negatives:
Abnormal cells may be missed.
False positives:
Inflammation or infection can sometimes mimic abnormal cells.
Mild discomfort:
You may experience some discomfort during the procedure.
Despite these limitations, Pap tests are one of the most reliable tools for cancer prevention.
Do you need a Pap smear if you are a virgin?
In most cases, HPV is spread through sexual contact with your sexual partner, so the risk is lower if you have never had sex.
However, some guidelines still recommend routine Pap tests from age 25, since HPV can occasionally spread through non-penetrative contact or other rare routes.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and advice based on your unique situation, please consult a specialist at Thomson Medical. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Novena:
6592 6686 (Call), 8611 8986 (WA) - Bukit Batok:
6569 0668 (Call), 8686 3525 (WA) - Choa Chu Kang:
6893 1227 (Call), 8282 1796 (WA) Jurong:
6262 8588 (Call), 6262 8588 (WA)- Katong (female doctor):
6970 2272 (Call), 8611 9020 (WA) - Punggol:
6243 6843 (Call), 8811 0328 (WA) - Sembawang: 6753 5228
- Sengkang: 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): 6382 3313
- Tampines: 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: 6276 1525
