Detecting ovarian cancer early can make a big difference. It gives you more treatment options and a better chance of recovery. Although there’s currently no single test that can reliably detect ovarian cancer in its early stages, certain screening tools can help spot warning signs before the disease spreads.
In Singapore, there are several screening options available, including CA125 blood test, transvaginal ultrasound, pelvic exam and CT scan. Knowing how these tests work can help you feel more prepared and make an informed choice about your health.
What is ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the ovaries, the female reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs (ova) and hormones such as oestrogen and progesterone. The ovaries are almond-sized organs located on either side of the uterus in the pelvis.
When doctors talk about checking for ovarian cancer, they may use tests to look for early changes in the ovaries or to investigate symptoms that could be concerning. Unlike Pap smears for cervical cancer or mammograms for breast cancer, there isn’t currently a standard ovarian screening test that’s recommended for all women. This is because no single test is sensitive enough to reliably detect early-stage ovarian cancer.
However, screening is still available for women with certain risk factors, and early detection can significantly improve treatment options and outcomes. To get the most reliable results, your doctor may recommend a combination of different methods.
When do you need ovarian cancer screening?
You might be wondering: “Should I get screened?” The answer will depend on your personal risk factors. It’s best to talk to your doctor about screenings if:
You have a family history of ovarian cancer:
If your family member, such as your mother, sister or other close relative, has had ovarian cancer, your risk may be higher. Some families carry genetic mutations such as BRCA1 or BRCA2 that can increase cancer risk.
You’re over 50 years old:
Ovarian cancer is more common in women over 50. It’s rare before age 40, but it’s always beneficial to be aware of your risk.
You’ve never been pregnant:
Women who have never had children or had their first after age 30 may also have a higher risk.
You’ve had breast cancer, uterine cancer or endometrial cancer:
If you have had these types of cancer before, your chances of developing ovarian cancer may be higher.
You have symptoms:
If you notice any of these symptoms persisting for more than two weeks, don’t ignore them:
Persistent bloating
Pelvic or abdominal pain
Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly
Frequent or urgent need to urinate
Changes in bowel habits
Unexplained weight loss
These symptoms can be caused by many factors or conditions, but checking with your doctor will help ensure everything is okay and give you peace of mind.
Even if you have some of these risk factors, it doesn’t always mean you’ll develop ovarian cancer. However, understanding them can help you and your doctor make informed decisions about screening or prevention.
If you're unsure whether you need screening, or if you simply want to be more proactive about your reproductive system health, schedule an appointment with Thomson Medical. Our gynaecologists will assess your risk factors, answer your questions, and guide you through the screening process with care and expertise.
Ovarian cancer specialist
Loading...
Common ovarian cancer screening tests in Singapore
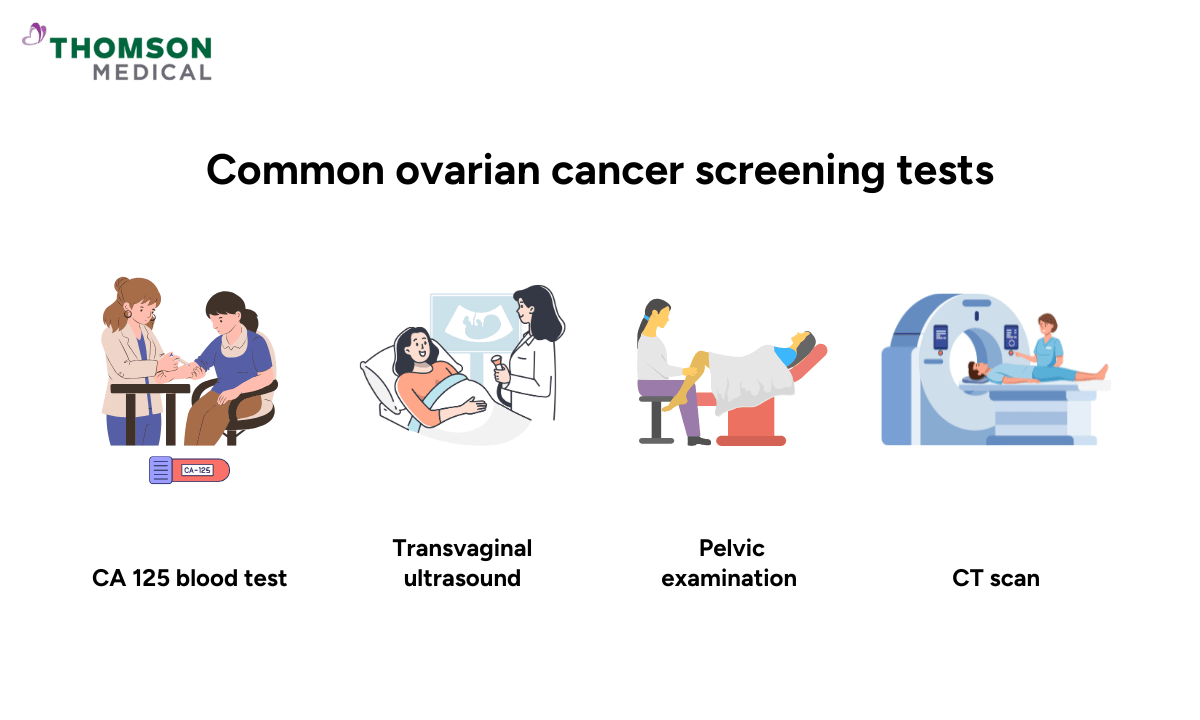
Several tests are available to assess your ovarian cancer risks. Your doctor will recommend the most suitable combination based on your specific situation for the best result.
CA-125 blood test
This test measures the level of a protein called CA-125 in your blood. When you have ovarian cancer, CA 125 levels in your blood are elevated.
However, this test has limitations. A high CA-125 marker can also be caused by non-cancerous (benign) conditions like endometriosis, uterine fibroids, menstruation or even pregnancy.
Because of this, the CA-125 test is mainly used to monitor how well treatment is working in women who already have ovarian cancer. It may also be used to keep track of women at higher risk, rather than as a routine screening tool for everyone.
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS)
During this test, a small probe is gently inserted into your vagina to create detailed images of your ovaries and surrounding structures. The transvaginal ultrasound can detect cysts, masses or other abnormalities in your ovaries and even fallopian tubes that might need further investigation.
An ultrasound can show if something looks unusual, but it cannot confirm whether a growth is cancerous or benign.
Pelvic examination
Your doctor will perform a physical examination, feeling your abdomen and pelvic area for any lumps, fluid buildup, or enlarged organs. Because ovaries are small and located deeply inside your body, it can be difficult to detect early-stage tumours through examination alone.
CT Scan
If initial tests suggest something abnormal, your doctor may order a CT scan to get a clearer picture of your abdomen and pelvis. This imaging test can help identify large masses, detect spreads, and monitor treatment responses. However, like a pelvic exam, a CT scan cannot detect cancer in its early stages.
What to expect before, during and after screening?
Knowing what happens during the screening can help you prepare better and ease any worries you may have.
Before the screening
There’s no special preparation needed for the CA-125 blood test or pelvic exam. However, for a transvaginal ultrasound, you should empty your bladder beforehand. You also need to avoid eating or drinking a few hours before CT scans.
For a more comfortable experience, wear clothing that’s easy to change, and let your doctor know about any symptoms you’re experiencing and any questions you may have.
During the screening
Each test will have a different procedure. There is nothing to worry about because your doctor will gently guide you through the screening.
CA 125 blood test:
The test is quick and usually lasts 5 minutes. Your doctor will take a small blood sample from your arm and send it to the laboratory to measure your CA 125 level.
Transvaginal ultrasound:
It lasts about 15 to 30 minutes. You’ll lie on an examination table while a small, lubricated probe is gently inserted into your vagina
The procedure is generally not painful, though you might feel some pressure.
Pelvic examination:
You’ll be asked to lie on an examination table with your feet in stirrups. Your doctor will gently examine your abdomen and pelvic organs. While it may feel a bit uncomfortable, it shouldn’t be painful.
CT scans:
The scan usually takes 10-30 minutes. You will lie on a table that slides into a doughnut-shaped CT scanner. The scan uses X-rays to take detailed images of your body from different angles.
After the screening
The results will be available within a few days depending on the type of test. Your doctor will discuss the results with you and explain what they mean.
If everything looks normal:
Your doctor will recommend when you should return for your next check-up based on your risk factors. This might be annually or every six months for high-risk people.
If there are abnormalities:
Don't panic. Many abnormalities are non-cancerous. For a more accurate diagnosis, your doctor may suggest:
Repeating the tests after a few months
Additional imaging or blood tests
A biopsy or surgery to examine the tissue more closely.
How much does ovarian cancer screening cost in Singapore?

The cost of ovarian cancer screening in Singapore can differ based on the clinic you visit and the tests you choose.
CA 125 blood test:
For a standalone test, the price usually ranges from SGD 20-30.
When it’s included in a package, the cost can range from SGD 200-300.
Transvaginal ultrasound:
A standalone transvaginal ultrasound costs around SGD 130 to 200.
However, if it is part of a health screening package, prices can vary a lot. A basic package can cost from around SGD 400, but more comprehensive screenings can cost SGD 3,200.
Pelvic examination:
This exam is usually included in comprehensive packages, which combine a pelvic examination, a Pap smear, a pelvic ultrasound and other tests. The price range from SGD 360-570.
CT scan:
It usually costs about SGD 400-600.
Some healthcare clinics provide comprehensive screening packages that include ovarian cancer screening. The exact price depends on the clinic and the range of tests included in the package.
For detailed fee information and payment options, please consult your healthcare provider directly. Schedule an appointment with our specialists at Thomson Medical today for a detailed price breakdown and a personalised care plan.
FAQs
What are the different types of ovarian cancer?
There are three main types of ovarian cancer:
Epithelial ovarian cancer:
This is the most common type, especially in women over 50. Most screening tests are designed to detect this type.
Germ cell tumours:
These are rare and usually affect younger women and girls. They often respond well to treatment when caught early.
Stromal tumours:
These are also rare. It develops in the cells that produce hormones in your ovaries.
Understanding which type you might be at risk for helps your doctor recommend the most suitable screening approach, and if cancer is found, develop the right treatment plan for you.
Treatment options can vary depending on your cancer type and stages of ovarian cancer at diagnosis, but they usually include surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and hormone replacement therapy.
Is ovarian cancer screening necessary if I have no symptoms?
For most women without risk factors, routine ovarian cancer screening isn’t currently recommended. This is because available tests can produce false positives (suggesting cancer when there isn’t any) or false negatives (missing early cancer), leading to unnecessary worry or procedures.
However, if you have risk factors, such as BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations or a strong history of ovarian or breast cancer, screening may be beneficial even without symptoms. If you’re unsure whether a screening test is for you, discuss with your doctor to make a decision.
How often should I get screened?
The frequency of ovarian cancer screening depends on your risk level:
Average risk:
If you don’t have any symptoms or a family history, there is no need for routine screening. Instead, it’s better to focus on annual gynaecological check-ups.
High risk:
You are at high risk when you have BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations or a strong family history. In this case your doctor may suggest a screening test every 6-12 months, especially at age 30-35. This may include CA-125 blood tests and transvaginal ultrasounds.
If you have concerning symptoms:
It’s best to see your doctor promptly for evaluation, regardless of your last screening.
It’s completely normal if you feel overwhelmed, but don't worry, your doctor will help you create a personalised screening schedule based on your situation.
Are there any risks or side effects of screening?
The screening tests themselves are generally safe with minimal risks:
You might experience slightly discomfort during the pelvic exam, ultrasound or CT scan
In some cases, women feel a bit of cramping after a transvaginal ultrasound
There may be minor bruising at the blood draw site
How soon can I get my results?
The timing of your results can vary depending on the type of tests you’ve undergone. In most cases, you can expect to receive them within a few days to two weeks.
Your doctor will schedule a follow-up appointment to discuss your results and any next steps. If you feel anxious while waiting for the results, don’t hesitate to contact your doctor. They understand the wait can be a stressful time.
How long can a woman have ovarian cancer before noticing it?
Women can have ovarian cancer for several years without realising it. That’s why this disease is called a “silent killer”.
Ovarian cancer can go undetected because the early symptoms are usually vague and easily mistaken for digestive issues, stress, or other conditions. The average time from first noticing symptoms to diagnosis is about 7-8 months globally.
Early-stage ovarian cancer is usually confined to the ovaries, but as it progresses, cancer cells can spread to the fallopian tubes, lymph nodes, and other areas. That’s why early detection can make a big difference.
So if you experience persistent bloating, pelvic pain or urinary changes for more than two weeks, it’s best to consult your doctor.
Can a Pap smear detect ovarian cancer?
No, a Pap smear cannot reliably detect ovarian cancer. Instead, it’s usually used to detect cervical cancer.
The information provided is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and tailored advice based on your unique situations, please consult a specialist at Thomson Medical. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical today.
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Novena:
6592 6686 (Call), 8611 8986 (WA) - Bukit Batok:
6569 0668 (Call), 8686 3525 (WA) - Choa Chu Kang:
6893 1227 (Call), 8282 1796 (WA) Jurong:
6262 8588 (Call), 6262 8588 (WA)- Katong (female doctor):
6970 2272 (Call), 8611 9020 (WA) - Punggol:
6243 6843 (Call), 8811 0328 (WA) - Sembawang: 6753 5228
- Sengkang: 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): 6382 3313
- Tampines: 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: 6276 1525
Dr Ryan Lee Wai Kheong
Obstetrics & Gynaecology (O&G)
Thomson Specialists Woodleigh (Women's Health)
English, Mandarin
Prudential, Great Eastern, Adept, MHC and 4 others

