Unexpected vaginal bleeding can be unsettling, whether it happens between periods, after menopause, or simply feels heavier than usual. Many women assume these changes are due to hormones, stress, or other common causes. However, this is not always the case.
Ovarian cancer itself does not usually cause vaginal bleeding directly. However, in some cases, tumours can influence hormone levels or nearby organs, leading to unexpected changes.
Understanding when bleeding may be linked to something more serious, especially if it occurs alongside symptoms such as bloating or pelvic pain, can help you know when it is time to seek medical advice.
What is ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer develops in the ovaries, the organs in your pelvis that produce eggs and hormones. It's sometimes called a "silent" disease because it doesn't always cause obvious early symptoms.
Many women don't notice warning signs until the disease has progressed, especially since the symptoms can be easy to miss or mistake for another health issue. This is why recognising unusual changes in your body, including unexpected bleeding, is important.
Does ovarian cancer cause bleeding?
Vaginal bleeding isn't the most common sign of ovarian cancer, but it can happen. Most abnormal bleeding is linked to other conditions like hormonal changes, uterine fibroids or endometrial polyps.
When ovarian tumours grow larger, they may press against your uterus or nearby organs, which can sometimes cause unexpected vaginal bleeding.
If you're over 40 or past menopause and notice any new bleeding, it's worth getting checked. While it can feel worrying, most causes are not cancer. Your doctor can examine you, run tests if needed, and explain what's causing the bleeding. Getting answers helps put your mind at ease.
Ovarian cancer specialist
Loading...
What types of abnormal bleeding should I watch for?
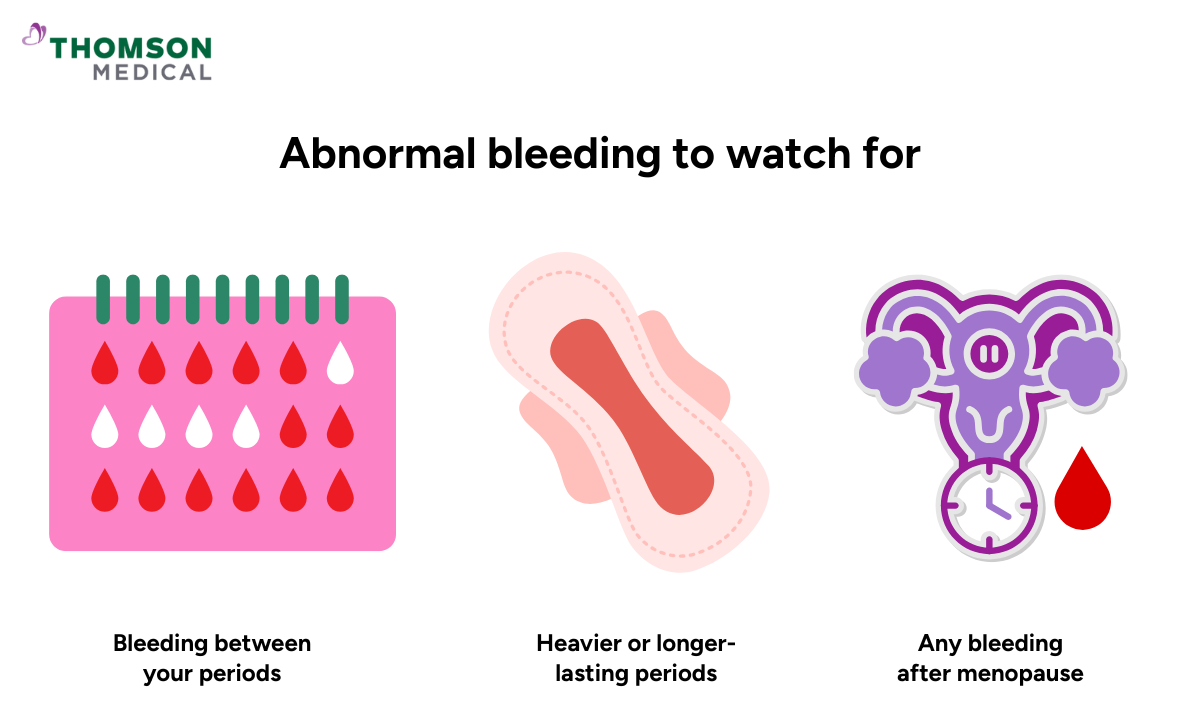
Abnormal bleeding can show up in different ways. Look out for:
Bleeding between your periods
Periods that are heavier or last longer than usual
Any bleeding after menopause
Spotting after sexual activity
Most of the time, abnormal bleeding isn't cancer, so try not to worry too much. However, if you notice any of these changes, especially if they're new or different from your usual pattern, it's worth discussing with your doctor.
Changes in bleeding patterns should be checked, even if they seem mild. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical to discuss your symptoms and get a proper assessment so any underlying cause can be identified and managed early.
Can ovarian cancer change my menstrual cycle?
Your periods might behave differently if ovarian cancer is affecting your ovaries. You could notice irregular period cycles, spotting when you don't expect it, or periods that are heavier or last longer than you're used to.
These changes happen because ovarian tumours can interfere with hormone production. It's important to know that many things can affect your cycle, so try not to panic if you notice something different. However, new or unusual patterns are worth mentioning to your doctor so they can check what's causing them.
What other symptoms might I experience?
Ovarian cancer can cause symptoms that are easy to mistake for everyday health issues. You might experience:
Persistent bloating or swelling in your abdomen that doesn't go away
Abdominal or pelvic pain that doesn't ease
Feeling full quickly when eating or loss of appetite
Changes in bowel habits, including constipation or indigestion
Feeling more tired than normal
Sudden weight changes
Changes in urinary habits, like feeling the need to urinate more often
If you've had any of these for more than two weeks, or they're happening most days, see your doctor. While these symptoms can have many causes, getting checked gives you answers. If treatment is needed, catching things early gives you the best chance of successful outcomes.
Am I at higher risk for ovarian cancer?
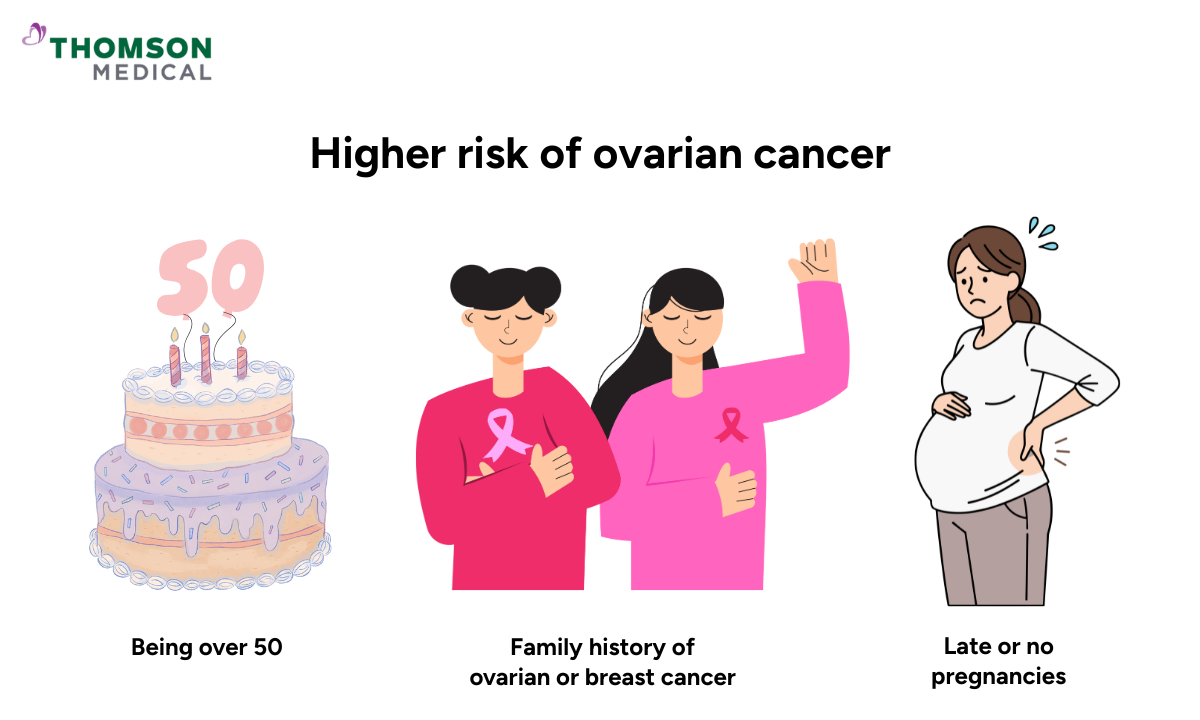
While anyone with ovaries can develop ovarian cancer, some factors may increase your risk:
Being over 50 (most cases happen after menopause)
Having a family history of ovarian cancer or breast cancer
Carrying genetic mutations like BRCA1 or BRCA2
Never having been pregnant or having your first pregnancy later in life
Starting periods early, late menopause, or using certain hormone therapies
If any of these apply to you and you're noticing unusual bleeding, tell your doctor about your risk factors. This might feel discouraging, but sharing this information helps them give you the best possible care.
They may recommend additional tests or closer monitoring, especially if cancer runs in your family.
How will my doctor investigate abnormal bleeding?
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, then perform a pelvic examination to check your ovaries and uterus.
Depending on the result of the examination, they might also recommend:
Imaging tests like an ultrasound or CT scan to view your ovaries and uterus
Blood tests, including a CA-125 blood test, which can sometimes show changes linked to ovarian cancer
A biopsy or minor surgery in certain cases to examine tissue more closely
Your doctor will help you choose the right tests based on your individual situation. They'll answer your questions, explain each step, and guide you through what comes next. Whether you need further tests or treatment, you'll have support throughout.
Understanding the cause of abnormal bleeding starts with proper testing. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical to get a personalised evaluation, discuss the recommended investigations, and plan the next steps with your doctor clearly explained.
FAQ
Is vaginal bleeding an early sign of ovarian cancer?
Vaginal bleeding can sometimes occur with ovarian cancer, but it's not an early sign. Most early-stage ovarian cancers don't cause obvious symptoms. More often, abnormal bleeding is caused by hormonal changes, fibroids or polyps. Any unexpected bleeding should be checked by a doctor, especially if it's new for you.
Can ovarian cancer cause bleeding after menopause?
Yes, ovarian cancer can sometimes cause bleeding after menopause, though it's not common. Any bleeding after your periods have stopped needs medical attention. It could point to several conditions, including ovarian or uterine cancer. If you notice this, see your doctor.
How can I tell if my abnormal bleeding is due to cancer or hormones?
You can't tell on your own. Hormonal changes, stress, thyroid issues or birth control can all cause irregular bleeding. The symptoms can look similar to those caused by cancer. Your doctor will use your medical history, age and test results to find the cause.
What tests are done to find the cause of bleeding?
Your doctor may start with a pelvic test, then use imaging tests like a transvaginal ultrasound or CT scan. Blood tests, including CA-125, may help identify changes linked to ovarian cancer. In some cases, a biopsy or minor surgery is needed. The tests will depend on your situation.
Can ovarian cysts also cause bleeding?
Yes, ovarian cysts can sometimes lead to irregular bleeding. Some cysts affect hormone levels, which may cause spotting or changes in your cycle. Others can rupture or irritate nearby tissue, causing bleeding or discomfort. Most ovarian cysts are benign, but symptoms that persist should be checked.
Should I worry about irregular periods if I'm under 40?
Irregular periods are very common in women under 40. They're usually caused by hormonal changes, stress or lifestyle factors. In most cases, they're not a sign of cancer. See your doctor if your periods are unusually heavy, last much longer than normal, or come with ongoing abdominal bloating, pelvic pain or sudden weight changes.
What should I do if I notice unusual bleeding?
Schedule an appointment with your doctor if you notice any bleeding that's unusual for you. Keep track of when it occurs, how heavy it is, and any other symptoms you're experiencing. This information will help your doctor work out what's happening and decide on the next steps.
The information is intended for general guidance only and should not be considered medical advice. For personalised recommendations and advice based on your unique situation, please consult a specialist at Thomson Medical. Request an appointment with Thomson Medical today.
Reference:
Lurie, G., Thompson, P. J., McDuffie, K. E., Carney, M. E., & Goodman, M. T. (2009). Prediagnostic symptoms of ovarian carcinoma: A case-control study. Gynecologic Oncology, 114(2), 231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2009.05.001
For more information, contact us:
Thomson Specialists (Women's Health)
Thomson Women's Clinic (TWC)
- Novena:
6592 6686 (Call), 8611 8986 (WA) - Bukit Batok:
6569 0668 (Call), 8686 3525 (WA) - Choa Chu Kang:
6893 1227 (Call), 8282 1796 (WA) - Jurong:
6262 8588 (Call), 6262 8588 (WA) - Katong (female doctor):
6970 2272 (Call), 8611 9020 (WA) - Punggol:
6243 6843 (Call), 8811 0328 (WA) - Sembawang: 6753 5228
- Sengkang: 6388 8125
- Serangoon (female doctor): 6382 3313
- Tampines: 6857 6266
- Tiong Bahru: 6276 1525
Notice
The range of services may vary between TWC/TS locations. Please contact your preferred branch directly to enquire about the current availability.
Request an Appointment